Grab has been acclaimed as the leading super-app in Southeast Asia due to their phenomenal growth and essential services offered during the pandemic. However, it was on the news headline during the past week for both good news and bad news:
Grab & Singtel have joint forces to launch the latest digital bank in Singapore – GXS digital bank
- Time to buy Grab stock?
Grab’s share price tumbled about 70% since its IPO.
- Time to sell Grab stock?
With the news grabbing the limelight, investors are wondering if now is the perfect time to invest in this super app company.
In this article, we will deep dive to find out if there is growth potential in Grab and should we invest in this leading super app!
GRAB BACKGROUND
Grab Holdings Ltd. (Grab) is Southeast Asia’s leading super app platform which is known as the “Everyday Everything” app, where the app is deeply integrated into consumers’ daily lives for ride-hailing, payments and delivery.
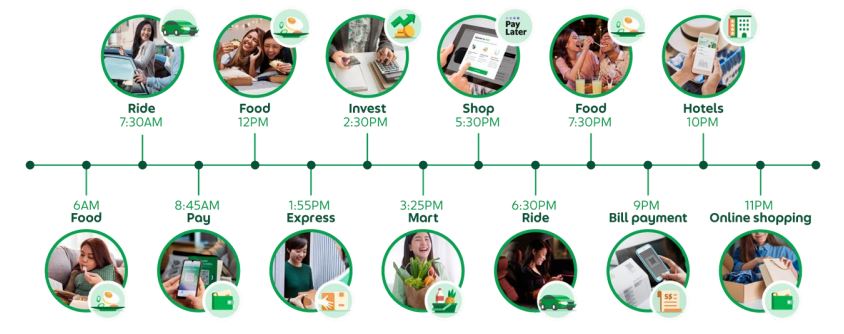
Grab, the “Everyday Everything” app that revolves around consumer’s daily lives
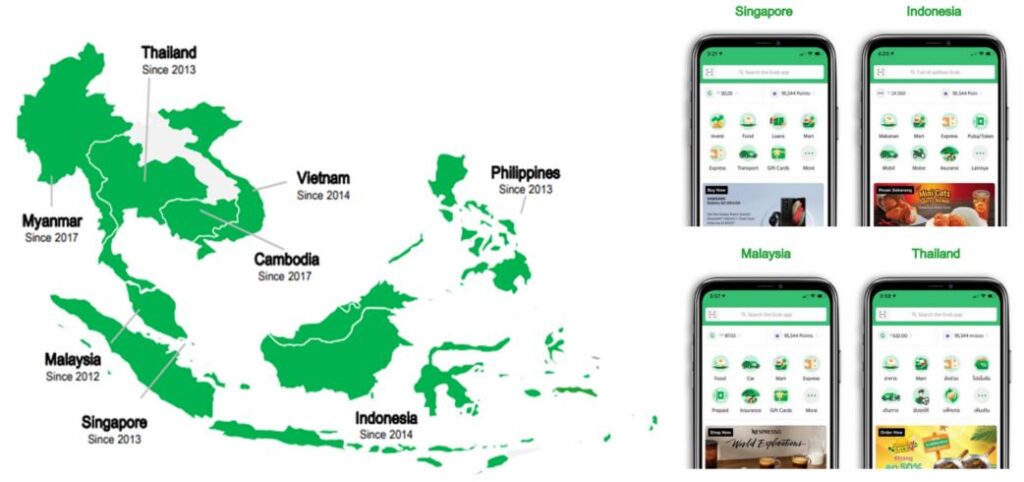
It operates across 8 Southeast Asian (SEA) countries in 480 cities that offer various services that cater to the localized needs of each country:
Besides working on business operations to generate profit, Grab is also a social enterprise. They introduce the term “Double bottom line” where they not only focus on the financial performance of the business operations but also provide a self-employed opportunity to their driver-partners to make a living.
In 2021, Euromonitor reported Grab as the category leader in the food delivery, ride-hailing and e-wallet segment. In the same year, Grab launched its initial public offering (IPO) in Dec 2021 at $13, with the ticker symbol – GRAB.
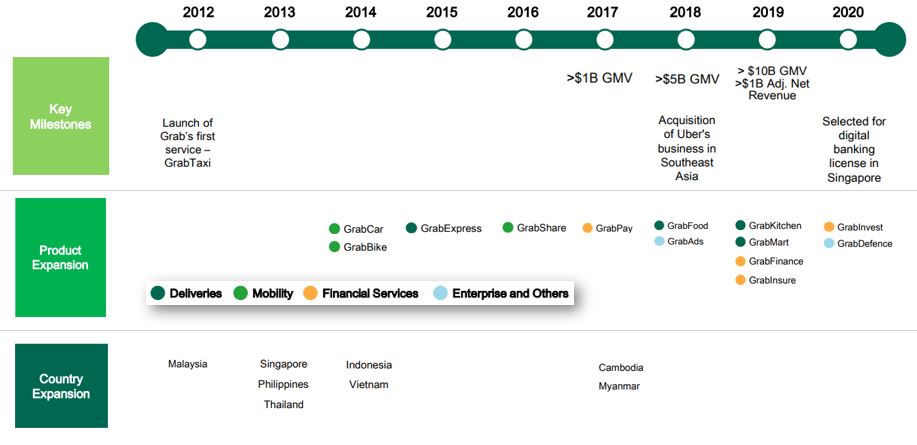
GRAB’S START-UP TIMELINE
The company was first founded as MyTeksi in Malaysia in 2012 where the founders want to provide a safe ride for the public as it was notoriously known that it was dangerous for ladies to take taxis at night during that period of time.

Since then, Grab kept on expanding its ride-hailing operations to other countries in the SEA region. Then subsequently expand their offering of more services for the public to use their platforms, such as food & grocery delivery and financial services.
The chart below illustrates the timeline of Grab from when they first started in Malaysia in 2012 as MyTeksi and business expansion in the SEA region until 2020 where Grab was awarded the digital banking license in Singapore.
PRODUCTS & SERVICES
Grab offers services across 4 different segments on their super app platform:

DELIVERIES
Grab offers delivery in 3 main product offerings – Food, Groceries and Package delivery.

Consumers can access these services via the Grab app and schedule the delivery according to their own convenience time. Whereas merchants can increase their digital customer base by offering their products on the Grab platform. Drivers can earn extra income by delivering the products on behalf of the merchants part-time or full-time.
MOBILITY
For mobility, consumers can easily book their ride from point A to point B in the comfort of their own home and jump on when the ride reached their designated pick-up point.

On the Grab platform, there is a wide variety of vehicles that the consumer can choose from, whether it is a private car, taxi or motorcycle (e.g. in Thailand and Indonesia). Besides making delivery, drivers who are involved in deliveries can also pick up consumers under the GrabCar to make additional income!
FINANCIAL SERVICES
Since launching their GrabPay services in 2017, this service has been expanding their offerings from e-wallet to MasterCard and Pay Later instalments, which allows a myriad of payment choices for consumers to pay for their goods & services.

In addition, Grab was able to obtain various financial licenses from the SEA countries to expand its financial services offerings, such as loans, investments, and insurance. When Grab-Singtel consortium was awarded the digital banking license by the Money Authority of Singapore in Dec 2020, they launched a new digital bank – GXS in Singapore (Sept 2022), offering banking services for the underbanked or financially underserved group.
ENTERPRISE AND NEW INITIATIVES
Grab offered their first enterprise product – GrabAds in 2018 to offer their merchant partners to advertise their products & services on the Grab platform (online advertising) or mobile billboard on their driver-partners vehicles (offline advertising).

In addition, the Grab platform also expands its offerings by having third-party service providers to offer their services, such as attraction tickets (Klook) and hotel bookings (Agoda, Booking.com) to Grab consumers.
By offering a wide range of services, the consumer can easily purchase their daily products and book rides or make payments on one single super app. It seems like Grab is gunning to maintain their lead as the super app that everyone loves to use in the SEA region! But do we know that Grab is the next superstock that we should look out for?
REVENUE GENERATION
Grab generated revenue mainly by earning commissions from their partners (driver & merchant). The diagram shows an example of how the revenue was generated from the Mobility and Delivery business segments.
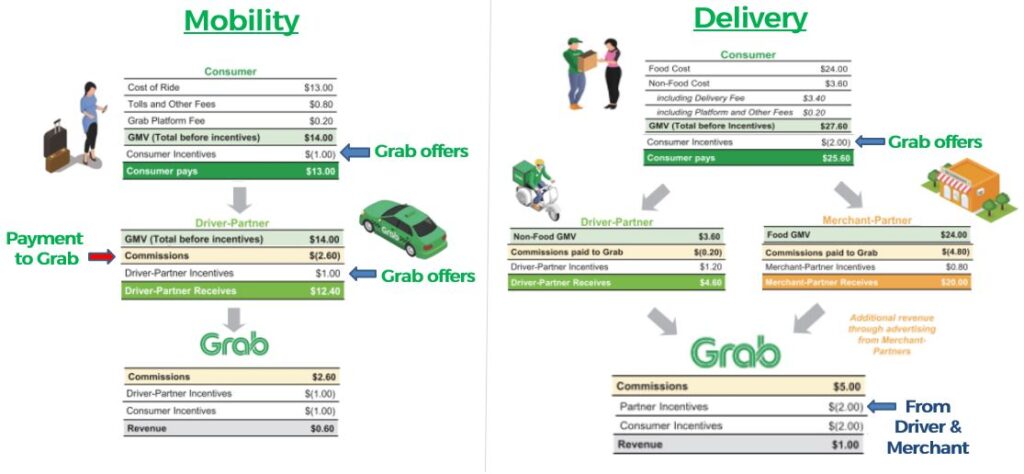
When a customer book a service or purchase a product from the Grab app, the driver/merchant partner will fulfil the order by picking up the customer (Mobility) or delivering the goods to the customer’s place (Delivery). Once the product or service has been delivered, Grab which provided the transaction platform for the services will charge a certain percentage of commission from their Driver-partner and Merchant-partner.
However, to attract customers and partners to use the Grab platform, Grab has also offered incentives or rebates to motivate them to use the app. After deducting the incentives from the commission earned, Grab will collect the remaining amount as revenue (shown in a grey-coloured box).

For the Financial Services segment, Grab charged transaction fees to their merchant partners when payment was done via the Grab payment platform. In addition, Grab also earns interest income from the loans provided. To learn more about what is interest income, Read more on our bank deep dive analysis!

Grab also generate revenue from advertising fees and commission fees by providing a platform for third-party service provider to sell their services.
Now, we will look into the numbers on how much revenue was generated by Grab in 2021 and the latest figure in Q2 2022!
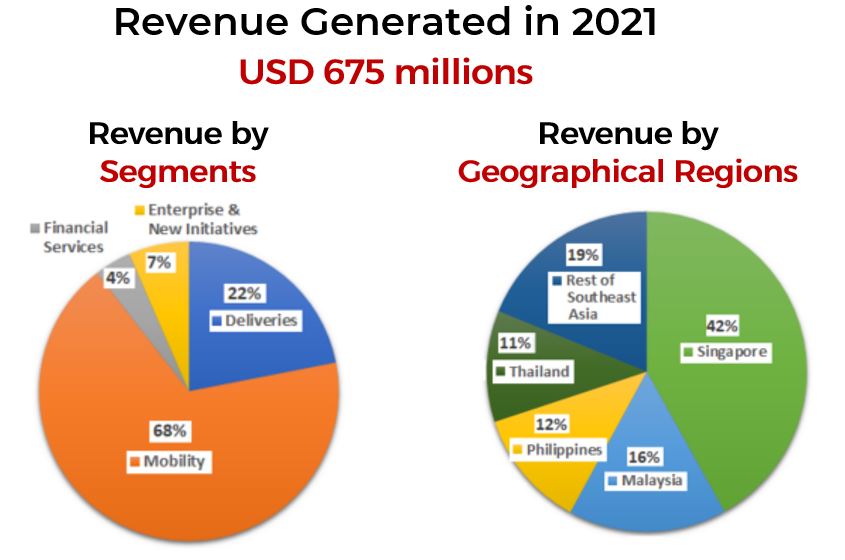
In 2021, Grab has generated a total of USD 675 million, where 68% of the revenue comes from Mobility, followed by Delivery (22%), Enterprise and New Initiatives (7%) and Financial Services (4%). Most of the revenue was generated from Singapore (42%). Malaysia has contributed 16% of the revenue in 2021, then the Philippines (12%), Thailand (11%) and the rest of SEA (19%).
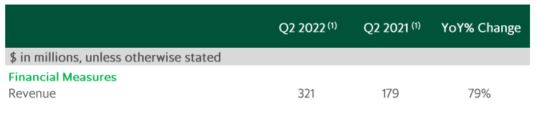
In Q2 2022, a total of USD 321 million was generated, about a 79% increment compared to the same period in Q2 2021.
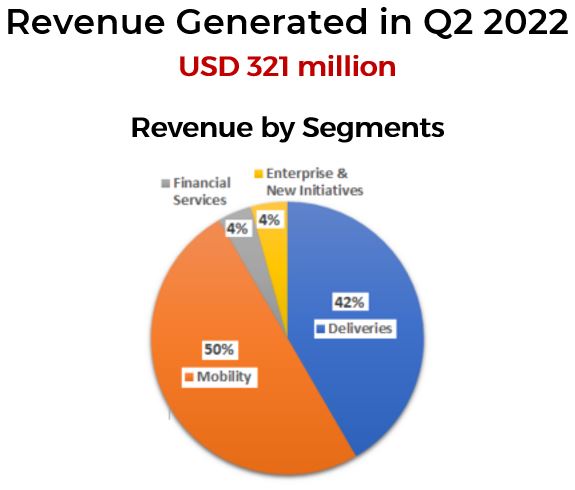
Even though we saw a drop in the percentage of the revenue generated by Mobility in Q2 2022 (50%) from the pie chart above, we noticed in their quarterly report that the revenue for the Deliveries segment (42%) had increased about 200% when compared against the previous year’s Q2.
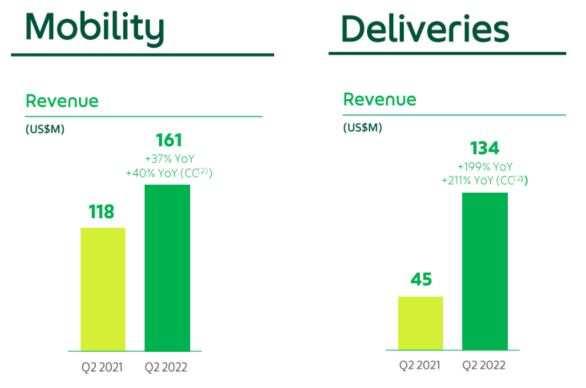
Thus, it was perceived that the Mobility business was slowing down in terms of percentage, but in financial numbers, both segments’ revenue has actually increased.
FUTURE PLANS
Grab has launched their monthly subscription plan – GrabUnlimited to entice the public to use its platform for their daily activities. By subscribing to 1¢ per month for the first 2 months, consumers can get $4 off for every delivery on GrabFood and GrabMart with GrabUnlimited.

To further expand its operations, Grab has expanded their network by acquiring Jaya Grocer, a mass-premium supermarket chain in Malaysia to offer on-demand delivery service to Malaysian customers.

In addition, Grab has also extended their partnership with Coca-Cola and Starbucks to extend its network coverage and offerings.

Both Grab and Coca-Cola plan to expand their digital customer base and accelerate the digitalization process with their merchant partners. Whereas for Starbucks, Grab is expanding the current service offering of GrabFood to Grab payments on their app ecosystem. They plan to expand these offerings to 6 SEA countries by 2024.
Grab collaborated with Singtel to provide digital finance services to the Singapore community when they were offered the digital banking license by the Money Authority of Singapore (MAS) in Dec 2020.

In Sept 2022, Grab-Singtel launched a digital bank – GXS that offers banking services to the financially underserved or unmet financial needs, such as SME entrepreneurs, gig workers and freelancers. The current banking services that are being offered are:
- Savings Account that accrued daily interest at 0.08% per annum
- Savings Pocket that accrued daily interest at 1.58% per annum
ECONOMIC MOATS
An economic moat is a competitive advantage that a company has over its competitors to maintain its market share and profit.
To stand above the rest of the super app platforms in the SEA region, they have a wide distribution network of delivery and mobility services that are available in 8 SEA countries. In addition, about 50 million stores worldwide accept GrabPay Mastercard which allows consumers easily pay for their products.
Currently, Grab has a large consumer network of about 32.6 million monthly transacting users (MTU) using the Grab platform, based on their Q2 2022 quarterly report.
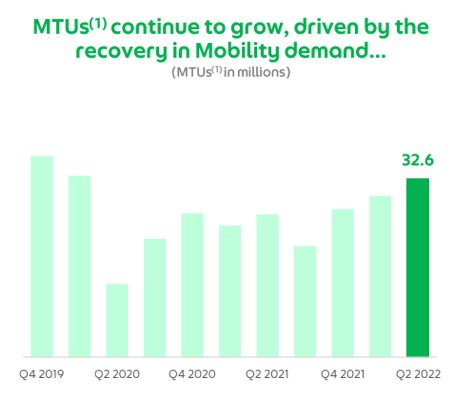
In Dec 2020, they were offered a digital bank license by MAS which allows them to offer more financial services to their customers, such as deposit accounts and loans.

In order to maintain its leading super app position in the SEA region, Grab will need to focus on consumer retaining strategies on their platform, which is also known as the stickiness factor such as brand loyalty and high switching costs.
For example, if the consumer enjoys using the Grab platform in their daily lives, let it be taking a ride, ordering delivery from their favourite food outlet or grocery, or even making the payment with their e-wallet or Mastercard, they may continue to use the current Grab platform and feel reluctant to switch to another super app platform for their daily lives activities.
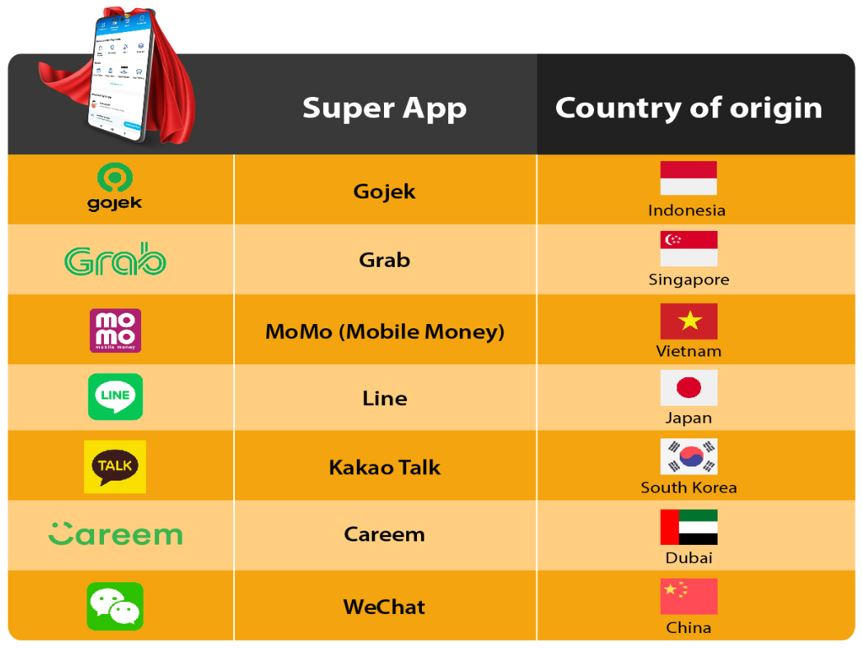
COMPETITORS
In the global region, different countries will have their own super app platform where it integrates seamlessly into consumers’ daily lives. The chart below shows the popular super app that is being used in different countries.
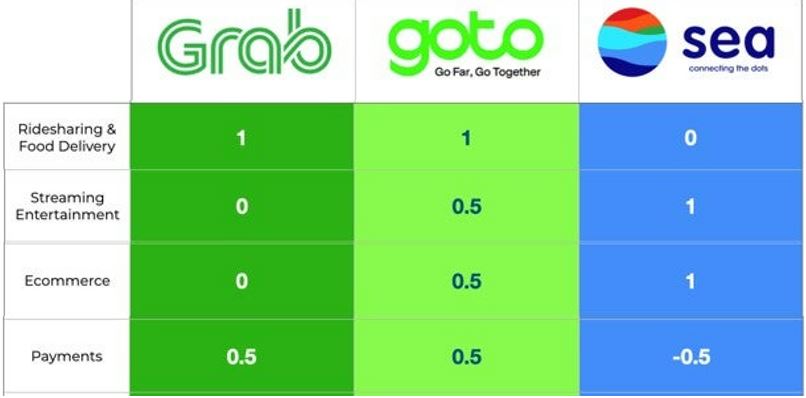
In the SEA region, we will compare 3 companies on the type of services that are being offered – Grab vs GoTo (Gojek) and Sea Ltd. One of the reasons that the other 2 companies were selected to compare against Grab was because they are able to offer payment services within the SEA region. (Sea Ltd. is the other company that was offered a digital bank license by MAS in Dec 2020!)
Entrepreneur.com
From the chart, we observed that Grab’s offering is mainly focused on ride-hailing, food delivery and payments, whereas Sea Ltd., they are offering streaming entertainment (Garena), E-commerce (Shopee) but currently there is no news on their plans to provide financial services. GoTo is the leading super app in Indonesia and it is involved in all the services mentioned.
With this in mind, we will further explore how well Grab competes against other app providers in food delivery competition and payment services.
During the Covid-19 pandemic, most countries are locked down to curb the pandemic from spreading and exacerbating the situation. As a result, most people are stuck at home.
This led to the rise of food delivery services as many people had to rely on delivery for their daily meals and groceries.
In 2021, Grab is the leading app for food delivery for most of the SEA region (except in Malaysia) based on GMV, as shown in the chart below:
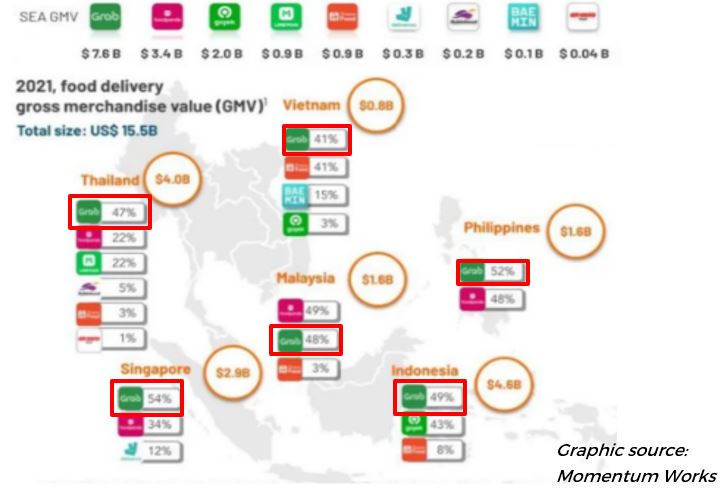
For the payment services offered, there are various modes of e-payment that a consumer can use to pay for their daily necessities in Singapore. Mobile wallet is also known as e-wallets. From the diagram shown below, GrabPay is in a stiff position to compete with other mobile wallet payments in Singapore.

We have made a deep dive analysis on another competitor of Grab in e-wallet – SEA Ltd. Read more on SEA Ltd.
After going through Grab’s exciting future plans and also analyzed on their competitors in the SEA region, Grab has some kind of competitive advantage and attraction that entice people to use its platform!
FINANCIALS
In this section, we will further investigate Grab’s financial numbers to determine if the company is currently profitable from its existing business activities.
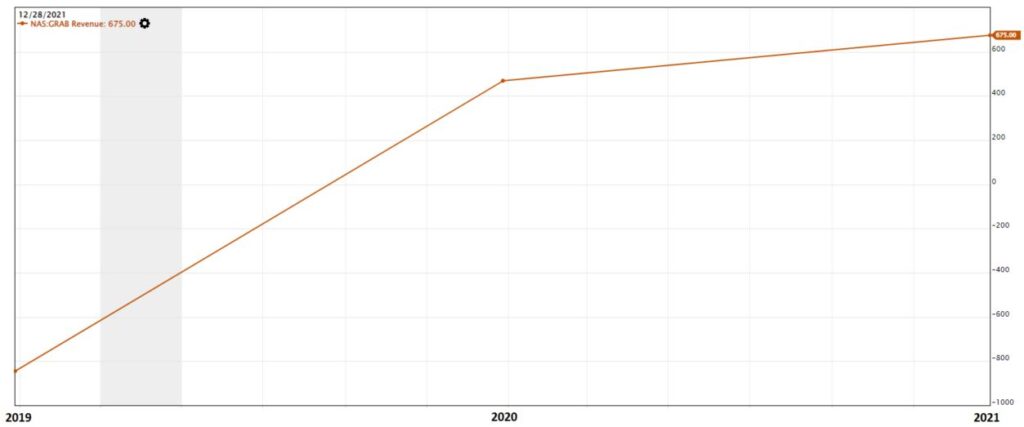
When Grab release their financial numbers in 2019, its Revenue was in the red but Grab managed to generate positive revenue in 2020 and the revenue continue to increase to USD 675 million in 2021, about a 44% increment. Revenue refers to the sales that the company generated from their business activities, it is not the profit or loss that the company has made.
However, when we checked on their Net Income, the company is currently experiencing losses as the net income is negative as per shown in the chart below.
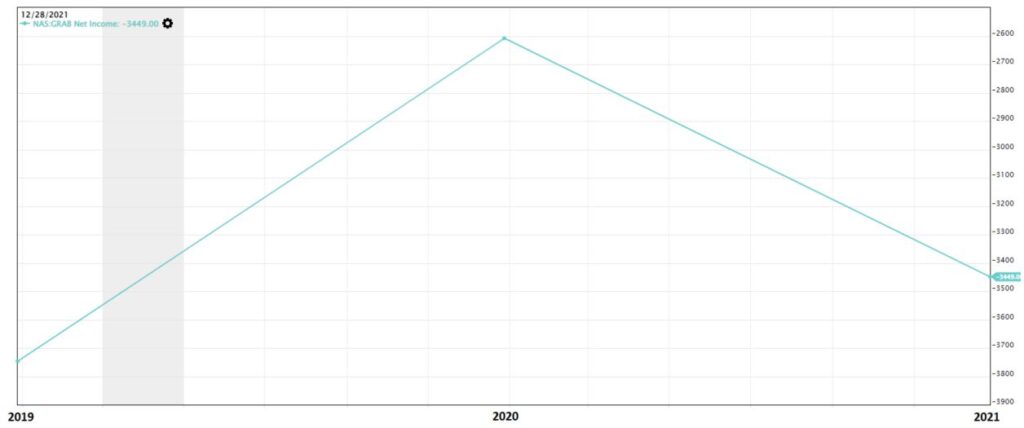
Net income is defined as the outcome of all expenses deducted from the revenue generated.

We are curious why was the company experiencing losses when they are generating positive revenue. With that in mind, we investigated their latest annual report and found that their expenses are higher than their revenue, which led to a deficit in their operating income and net income.
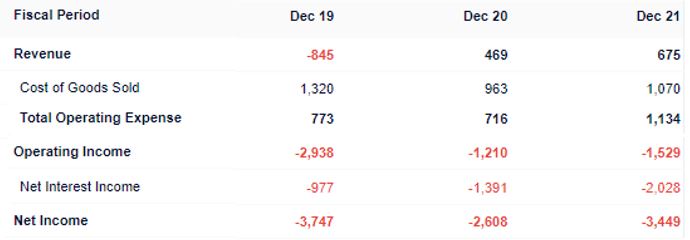
The expenses were high as the company is still in the expansion stage to gain market share. Thus, they were spending a lot on marketing activities, headcount expenses and consultation fees for the expansion operation. The high net interest income was due to their share listing expenses.
Next, we will check on the company’s cash flow situation. In the chart below, we observed that the Cash Flow from Operations, which is the cash flow generated from normal business activities was also negative.
- If the cash flow is positive, it means that more cash is flowing into the company.
- If the cash flow is negative, it implies that more cash is flowing out of the company.
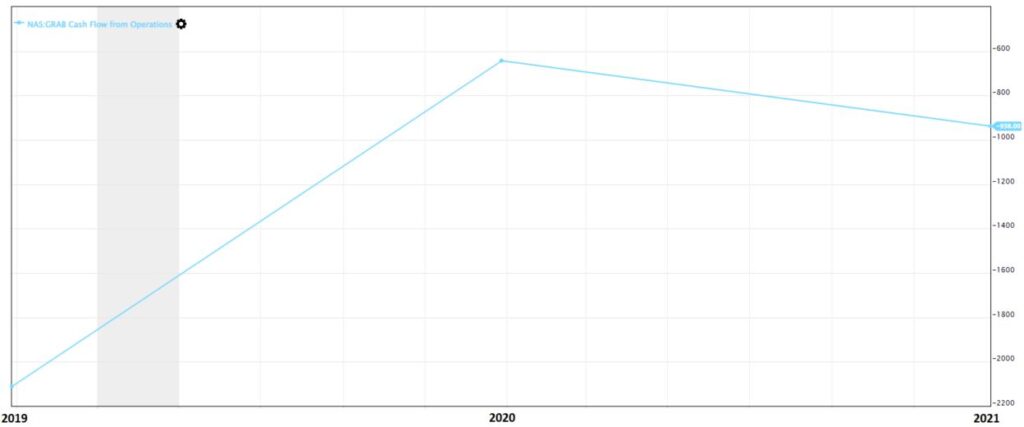
As the company is currently expanding and overspent on its expenses, more cash is flowing out compared to the cash flowing into the company from its business activities.
The other cash flow criterion that we will investigate is the Free Cash Flow, which is the cash flow that the company retains after deducting the expenses to purchase assets that last for more than 12 months, known as Capital Expenditure (CapEx).
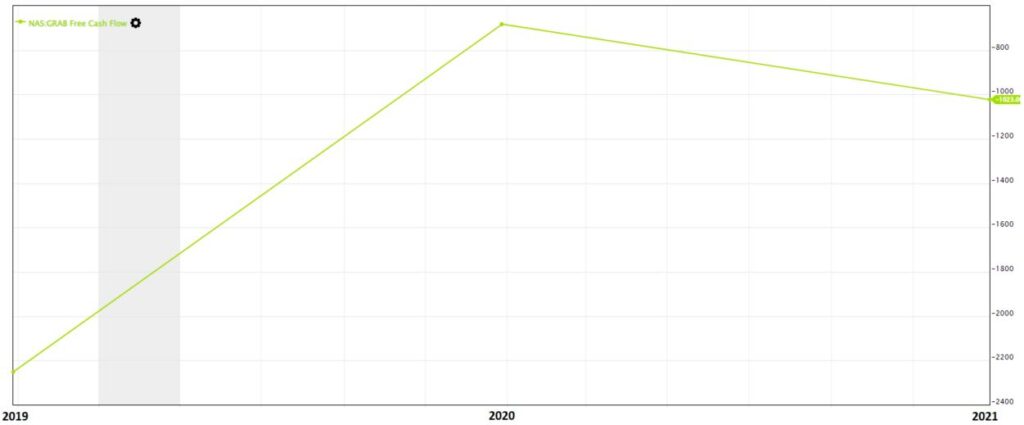
Based on the Free Cash Flow Chart, it is also negative as the company was having negative operating cash flow for the 3 years (2019-2021). In short, Grab is bleeding cash (cash flowing out) at the moment.
The next criterion that we investigated is to determine the debt level of the company and the financial criteria that we looked at are the Debt-to-Equity ratio. The mathematical formula of the Debt-to-Equity ratio is:

Based on the mathematical definition, for every $100 of equity, the company should not borrow more than $50 of debt. From the chart below, the current debt-to-equity ratio of Grab in 2021 is 0.28. According to the Value Investing methodology, Grab is currently not highly leveraged.
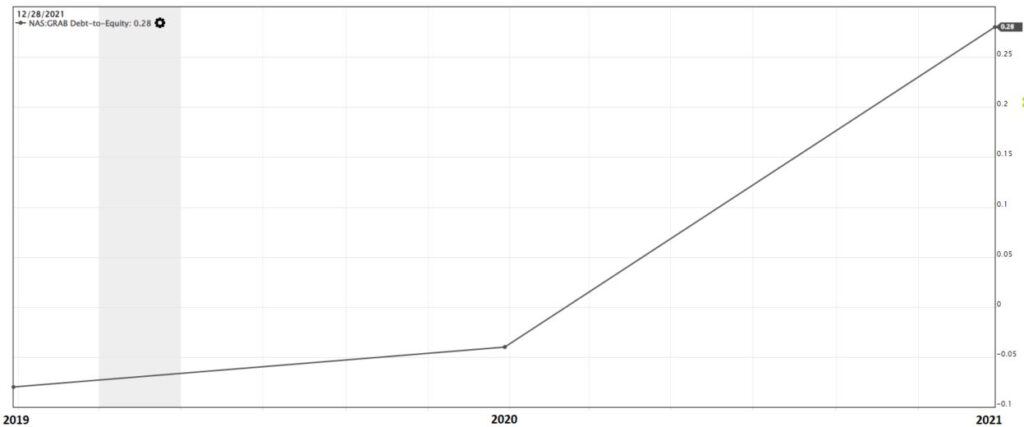
After a brief analysis of the company’s financial numbers, Grab is still not making money from its business activities. As such, we are wondering how long can the business sustain as there are bills to pay for the business operations but the company is currently bleeding money for expansion.
With this question in mind, we will also look at Grab’s balance sheet and check on their Shareholders’ Equity.
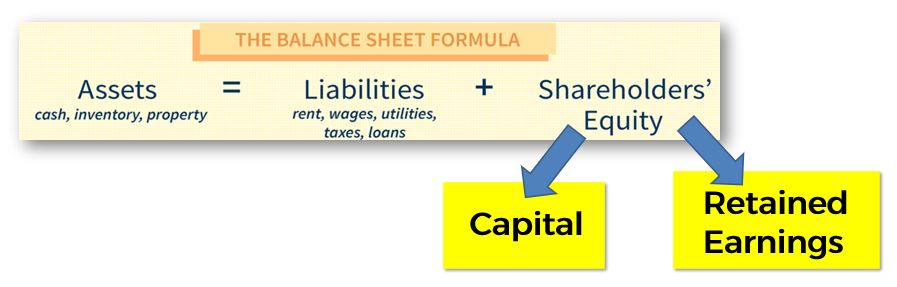
Shareholders’ Equity is mainly made up of Capital (money that the company’s investors poured into the business) and Retained Earnings (accumulation of income the company has generated from the business operations).
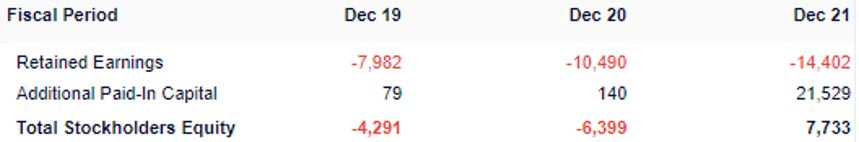
In their annual report, Grab is not able to accumulate earnings from their business operations due to the current cash outflow, which lead to negative retained earnings. However, the Shareholders’ Equity in 2021 is positive due to the huge inflow of capital from investors.
If the company is able to become profitable in near future, we will be able to observe positive retained earnings and not rely on capital inflow from investors to keep the business floating.
POTENTIAL RISKS
Currently, the company is in the red and not profitable since they release their financial report in 2019. In order to incentivize more consumers and partners to use their platform, they have been offering attractive incentives to build their market share which further exacerbates their cash-bleeding situation. In addition, the world is moving towards the endemic stage after the COVID-19 pandemic where people are able to go out and gather physically for dining, they may cut down their spending on food or grocery delivery. This will be another potential blow to revenue generation for Grab.
We also observed that Grab is in stiff competition with another super app that offers various services for the consumer to choose from. As a result, there will be low switching costs for the consumers as they can choose to go for the platform that offers the lowest price for the services that they are using, e.g. booking a ride.
Moreover, the new strategy launched by Grab may not work. One of the expansion strategies launched in 2020 was opening the ‘dark-store’ to sell groceries directly to consumers. A dark store is a micro-fulfilment centre for rapid online orders where they make it simple for online shoppers to receive goods that they purchased online.

However, due to the losses that Grab suffered for the past 2 years, Grab closed down its dark-store operation in 2022.

CONCLUSION
Grab is SEA’s leading super app platform which offers services in 4 different segments that are deeply integrated into consumers’ lives. It is also the category leader in the ride-hailing, food delivery & e-wallet segment in the region.
Nevertheless, investors will need to take note that currently the company is not profitable and experiencing losses due to the rapid expansion of its business operations. In addition, Grab is experiencing stiff competition against another super app in the SEA region.
DISCLOUSURE
The above article is for educational purposes only. Under no circumstances does any information provided in the article represent a recommendation to buy, sell or hold any stocks/asset. In no event shall ViA or any Author be liable to any viewers, guests or third party for any damages of any kind arising out of the use of any content shared here including, without limitation, the use of such content outside of its intended purpose of investor education, and any investment losses, lost profits, lost opportunity, special, incidental, indirect, consequential or punitive damages resulting from such unintended use.