NFT has been the hottest topic on the news where famous artists and social influencers bragged about their purchase of NFTs and high-profile sales of art pieces that worth millions of dollars with cryptocurrencies.
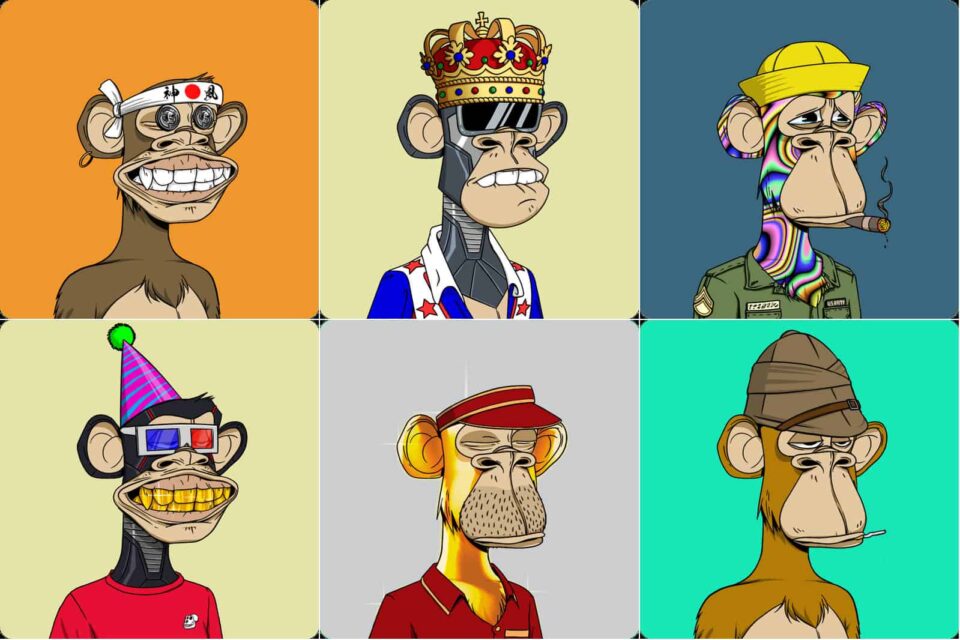
It seems like everyone is chasing after funky art pictures (ahem…Bored Ape, anyone? ), to show that they are in tune with the latest trend or owning something worth of astronomical value, a similar scenario like the Netherland’s tulip mania in the 17th century.

What is really NFT?
Why has it been the trendiest and most sought-after asset the past few months?
Today, we will dig deeper into the topic of NFT and see if it is worth to invest our hard-earned money just to buy some cool pictures for collection or speculation.
WHAT IS NFT?
NFT is an acronym for non-fungible token, a type of digital asset that represents real world objects like art, music, in-game items, and videos but exists only on blockchain. NFT can be bought and sold online, mostly via cryptocurrencies, e.g. Ethereum.

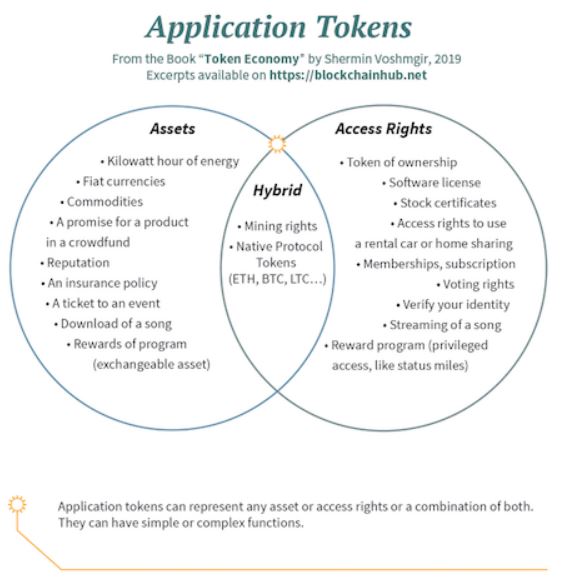
A token is a digital asset or access rights that can be used by the user. It is a set of rules that is encoded in a smart contract (will explain in later sections) and the smart contract is stored securely on the blockchain.
A cryptocurrency is a token secured by cryptography, but a token is not necessarily a cryptocurrency. In simplified terms, cryptocurrency is a subset of a token. Thus, a token can be anything from licenses (access rights) to a ticket to an event (assets).
WHAT IS THE DIFFERENCE BETWEEN FUNGIBLE AND NON-FUNGIBLE?
There are two types of tokens – fungible and non-fungible. How different are these two types of tokens?
FUNGIBLE
Every unit of cryptocurrency, bitcoin for example, is equal in value and has identical metadata. Thus, a fungible token can be used as a medium for commercial transactions, e.g. trade one bitcoin for another in exchange for product or services.
NON-FUNGIBLE
A non-fungible token has a unique identification metadata where every token is distinctive on its own and not interchangeable with another token. With its unique digital signature, NFT is like a digital passport or rare vintage wines where it cannot be exchanged at equivalency with other things. As a result of this, it created a sense of scarcity and rarity.

HOW DID NFT STARTED?
NFT was first created by Kevin McCoy and Anil Dash in 2014 as a “monetized graphics” to link artwork on on-chain metadata.
In 2015, the first NFT project, Etheria was developed on Ethereum blockchain.
Subsequently, it further evolved from ERC-721, a non-fungible token standard that was written in blockchain programming language (Solidity language) on Ethereum blockchain. This standard is used to create unique collectible tokens that contains ownership details, security and metadata which allows developers to tokenize ownership of any arbitrary data.
- A standard is a format or template that other Ethereum developers agree to follow when writing code to build tokens.
- ERC is acronym for Ethereum Request for Comment, a standard approved for usage by the Ethereum community.
- 721 is the proposal identifier number who propose for the standard application, in this case ERC-721 was proposed by Dieter Shirley, William Entriken, Jacob Evans and Nastassia Sachs.
In 2017, NFT started to gain popularity from the success of selling tradable cat NFTs from the CryptoKitties online games.

A SHORT DETOUR ON METADATA, ON-CHAIN VS OFF-CHAIN AND SMART CONTRACT
Before we delve deeper into the rabbit hole of NFT, there are a few terms we need to know in order to better understand the mechanics of NFTs. (In-depth explanations may be few pages long and end up dozing off halfway reading, zzz…).
We will KISS it– keep it short & simple and march on.
METADATA
Due to the rise of blockchain technology, metadata has been the trendiest word on search engines as people are trying to understand what metadata is. In short, metadata is the information that describes the data object which the information is linked to.
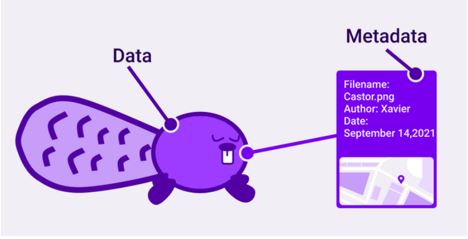
We can use a book as a simple analogy example to explain what metadata is. For the ease of locating a book in a huge library, the book cover contains information about the book title, author-name, publisher details, table of contents and index.

Metadata of NFT contains details of the NFT:
- Ownership details
- Properties of the digital asset’s
- Transactional history
NFT metadata can be represented on the On-chain or Off-chain.
ON-CHAIN & OFF-CHAIN
There are two types of metadata – On-chain and Off-chain (What’s the difference??)
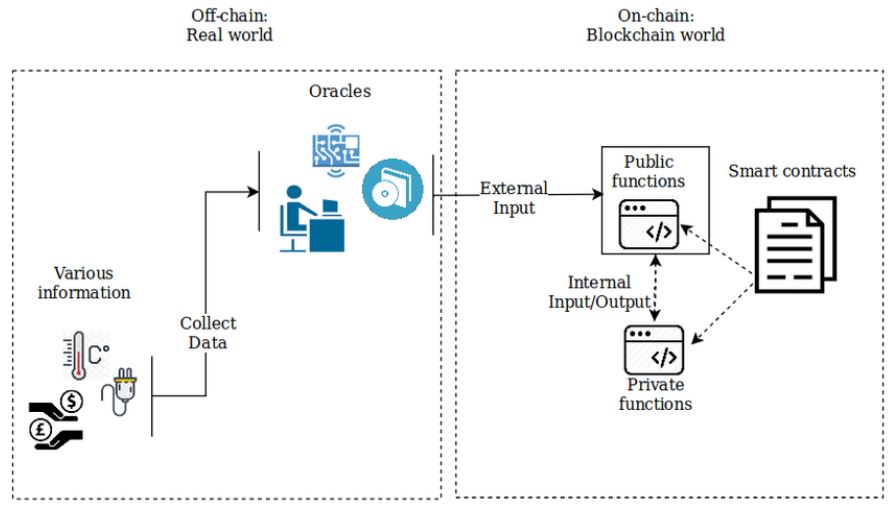
As the name implies, on-chain means that a digital asset is stored on the blockchain. It exists on the Blockchain world, for example, a smart contract (further explanation below).
Off-chain indicates that a digital asset is not stored on blockchain, it exists in the real world. The digital asset could be stored in off-chain storage like centralized servers, e.g. Amazon Web Services (AWS) or an InterPlanetary File System (IPFS), a type of peer-to-peer file storage system.
There are two types of NFTs – On-chain NFTs and Off-chain NFTs.
On-chain NFTs are NFT metadata directly incorporated into a smart contract of the NFT and stored on the blockchain. Thus, the NFTs origin can be easily verified and traced back to the original creator or owner on the blockchain, which is publicly accessible.
Off-chain NFTs are NFT metadata that is being hosted separately from the smart contract, so the metadata is not on a publicly accessible service such as the blockchain but in an off-chain storage system.
SMART CONTRACT
When we conduct any form of business transaction with another party, we tend to do business with someone we trust, or we will use a form of documentation, such as contract to hold each other accountable.
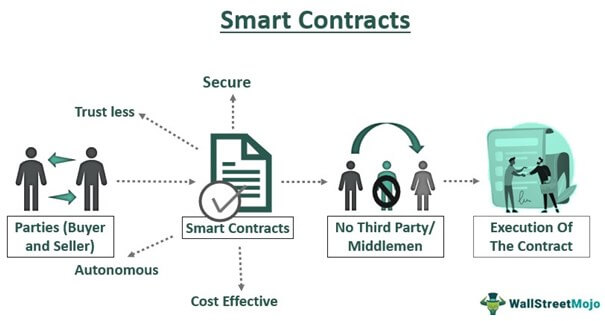
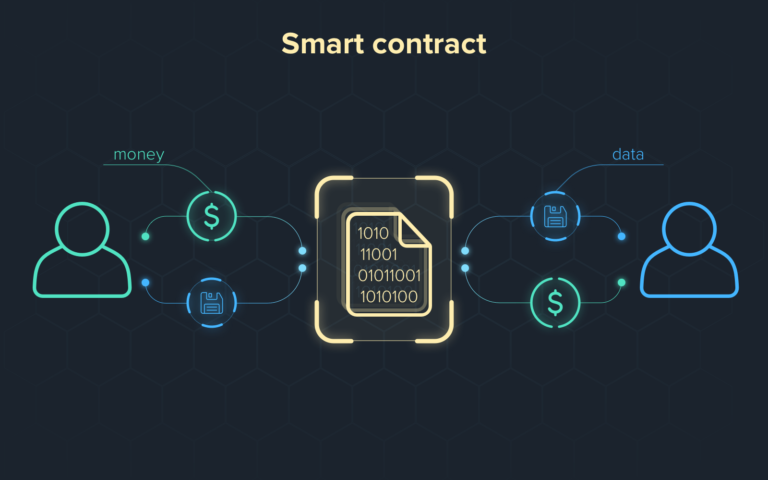
A smart contract is a form of self-enforcing agreement between two parties without intermediaries (peer-to-peer) by using code to execute the transaction.
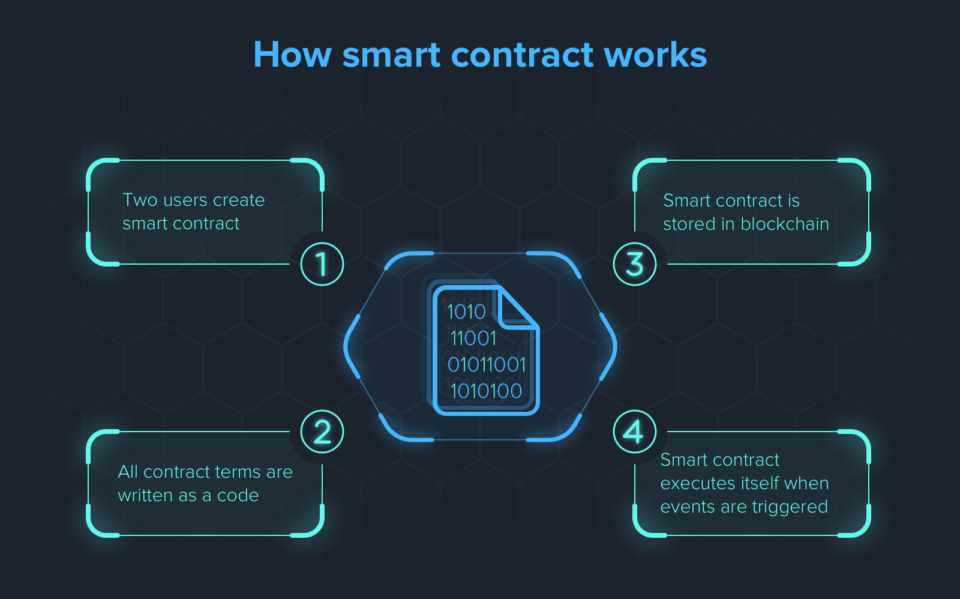
Smart contract uses code to write the contract terms and stored on the blockchain. The smart contract will execute the event when triggered by meeting certain prerequisites or conditional programming, such as an “if/then” situation. Each smart contract’s code is saved permanently on the blockchain, but the metadata of the smart contract can be directly incorporate into the smart contract (on-chain) or kept in a different location (off-chain).
For NFT, smart contract is the agreement document between the buyer and seller of the digital artwork where the smart contract contains a link that points to the server that stores the digital artwork and the NFT metadata that acts as a proof of ownership.
GAS FEE
And lastly, not forgetting about gas fee. What is a gas fee and how does it works?

A gas fee is the processing fees when minting smart contracts onto blockchain. Whenever a person uses the NFT marketplace platform to mint NFT or perform NFT transactions, they will need to pay gas fees.
Gas fee is in the unit of gwei and one gwei is equivalent to one nano ETH (0.000000001 ETH, that’s a lot of zeroooos). The diagram below shows an example of how the gas fee is charge when using the platform:
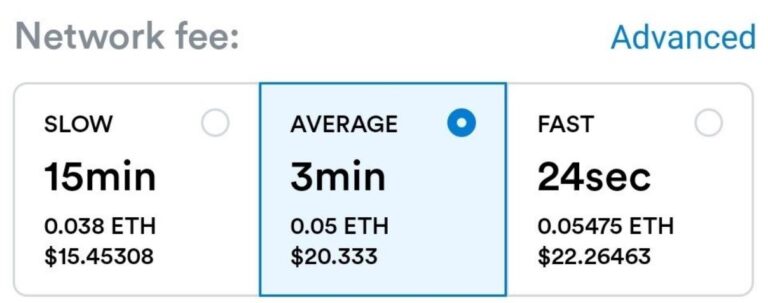
If one wish to have their token minted faster onto the blockchain, they will have to pay a higher gas fee as it will use up a lot more energy compared to the other rates.
HOW DOES NFT WORK AND ITS POTENTIAL USAGE?
Now that we got the relevant NFT terms squared away, we can move on to the fun part – how NFT works in the blockchain technology. Here, we will explore mainly about digital artworks of NFT as it is the hottest digital token and widely publicized on social media as of Mar 2022.
NFT was first created or “tokenized” on Ethereum blockchain by using ERC-721 standard, although there are some other blockchains (Cardano, Zilliqa, Solano) also start to support NFTs. Once the NFT is being created, it can be sold or traded on marketplaces such as OpenSea, Nifty Gateway and Rarible.
When there are interested buyers for the NFT, the creator or current owner may set a specific price or hold an auction for buyers to bid on the NFT with cryptocurrency. After the NFT has been successfully sold, both the current and new owners will create a smart contract to transfer the ownership of the NFT.
Every token of NFT is unique and not replaceable. Thus, it can only have one owner at a time and the non-fungible property allows NFT to be used as a certificate of authenticity or to convey rights over the digital asset.
Different types of digital assets can be tokenized, such as digital art, in-game items, domain names and even real-world items (event tickets, legal documents & signatures). Nike also use the NFT technology and own the patent – CryptoKick to authenticate sneakers as unique items.
COMPARISON BETWEEN NFT AND JPEG FILE
Currently, NFT is most widely used in digital media such as art works and videos. Newbies to the blockchain technology may confuse between JPEG image files with an NFT since both NFT and JPEG are image files.
What’s the difference between NFT and JPEG files?

Is this an NFT or JPEG?
Firstly, JPEG files can be created in infinite supply by using copy & paste function on digital tools, such as PC and smartphones. However, the creator of the JPEG owns the copyright of the art work. The JPEG can be enforced under law if it is trademark registered and the creator can sue the individual who use their creations for commercial use.
Due to its non-fungible properties, every NFT is unique, and thus the original copy cannot be easily duplicated. (The duplicate copy of NFT is a counterfeit!). In addition, the NFT transaction can traced back to the owner who purchase it as the metadata contains built-in authentication to serve as proof of ownership. Only one person can own the original of the art or digital media and this unleashed the “digital bragging rights” frenzy on social media.
However, NFT ownership is not equal to copyright or own the intellectual property rights to the NFT. New owners of NFT has to take note on the difference between ownership and copyright. Owners of NFT only owns the digital asset but they do not have the copyright to mass produce NFT like the original creators. This will be further discussed in the later part of the Risks section.
HOW TO MAKE MONEY ($$$) FROM NFT?
With the blockchain technology on the rising and NFT gaining popularity with high profiles sales – millions of dollars being spent on digital artworks and memorable videos; everyone is talking about the big money involved. Some even jumped on the bandwagon, hoping to make quick bucks from NFTs.

One of the most popular methods to make money from NFT is by selling digital artworks on a marketplace, such as OpenSea and Rarible. This allows artists to sell and monetize their artwork directly to consumers without intermediaries who usually take a cut from their profits.
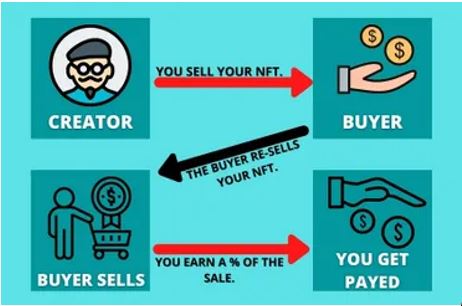
In the conventional method, once the artwork has been sold to the first buyer, the artist will no longer receive any future profits when the artwork was sold to another new owner. However, with NFTs, artists can receive royalty or future proceeds for their work every time their creation is being sold or changes new owner.
With the hysteria of huge profits being made in NFT, people are trading NFTs over the NFT trading platforms. However, not all NFTs are equal; some may worth millions, but some are worthless. Due diligence is a must if one intends to trade in NFTs and make a profit from it.

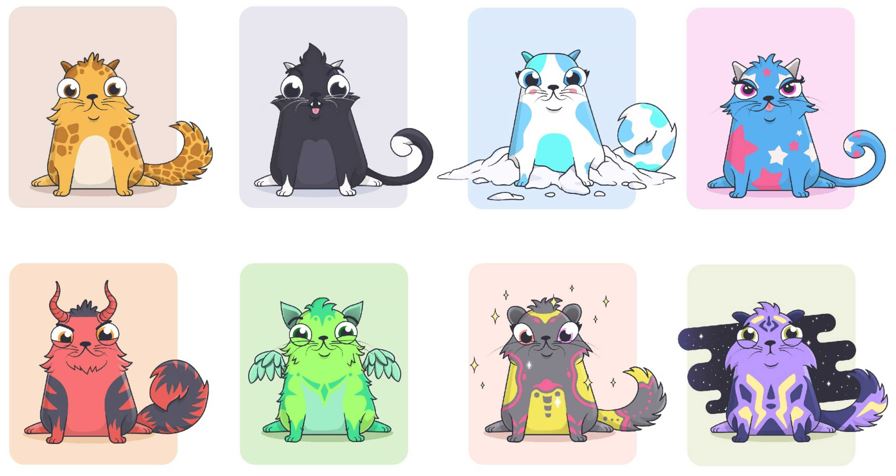
One can also make money from playing NFT games. Gamers will invest huge amount of money to buy and trade in-game objects, for example, CryptoKitties.
CryptoKitties is a blockchain-based games where gamers can collect and breed cute creature-like cats. Each cat is unique and 100% owned by its owner which cannot be replicated (created from ERC-721 standard). Two CryptoKitties can breed and produce an offspring with different properties from its parents. The gamers can then trade the unique cats with other gamers and make a profit, a term known as Play-to-Earn (P2E).
NFT staking is another new way to earn money in the NFT world. NFT staking is a practice of keeping the NFTs in the form of stake – storing collection of the tokens on platforms and receive rewards or other benefits from the platform. This allows the owners to earn income from their NFT collection while keeping their ownership.
WHY IS NFT SOOO HOT HOT HOT?
WHAT’S THE HYPE?
Sizzling news about NFTs being sold for millions of dollars, such as Bored Ape Yacht Club (BAYC) artworks and NBA Top Shot moments, had created frenzy headlines in the crypto communities for the past few months in 2021. This has created a lot of noise and hype about NFT is going to revolutionize the way of art collecting and a possible asset for investment, just like Picasso’s artworks or Da Vinci’s Mona Lisa.
The excitements about cryptocurrency and huge profits made from trading in crypto also give rise to the sensationalism of NFTs and everyone is talking excitedly about it over social media, especially the potential high profit margins that they can earn from getting involved in NFTs.

Nyan Cat GIF-file
High profile sales like the Nyan Cat, a 2011-era GIF file cat with a pop-tart body was sold for nearly $600,000 in February 2021.
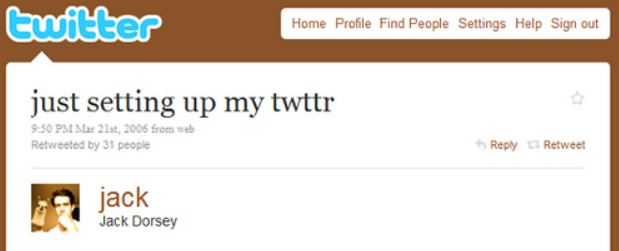
Twitter’ CEO Jack Dorsey sold his first ever tweet, “just setting up my twttr,” for about $2.9 million in Mar 2021. Celebrities are also releasing their unique moments and artworks as securitized NFTs to monetize them.
NFT metadata contains valuable information such as ownership details and proof of authenticity of the artwork. Duplicates of the artwork without metadata details are counterfeits that hold no value. A perfect example to illustrate this point is Da Vinci’s famous artwork, Mona Lisa.
There are many different reproductions of Mona Lisa but only the original one that is being created by Da Vinci himself holds value. This concept applies to NFT that the original artwork is not only high in resolution, but also has digital proof of authenticity and all transactions history of the artwork, stored in the metadata.
Due to its unique and irreplaceable nature, NFT has created a kind of digital scarcity where only one person can own the original piece of artwork. The value of the NFT is being determined by demand – the more it’s seen online and shared, the more popular and valuable it becomes among the community where people desire to own it. The person who owns that particular NFT can then display proudly on their social media or digital channels which reflects his or her status among the community, like owning a Rolex or driving a Ferrari on the street.
With the uniqueness feature, people will want to take NFT as an investment tool, using wait and HODL strategies like an “original” fine art in the museum that accrued value over time. When the value of the NFT increases, they can sell it at a high price, raking in millions to billions.
In addition to rarity of the NFT, many projects also offer additional perks like access to an exclusive club, or commercial rights to the art. To further understand about the hype of NFT, we will have a glimpse of BAYC (Bored Ape Yacht Club), the hottest NFT craze on the planet right now.

CASE STUDY – BORED APE YACHT CLUB
BAYC was founded by four Yuga Labs creators, with their pseudonyms – Gargamel, Gordon Goner, Emperor Tomato Ketchup and No Sass. They created only 10,000 ape NFT arts in circulation on Ethereum blockchain, with the intention of creating a privileged community club.
BAYC has been taking the internet by storm since it launched in April 2021, with many celebrities and athletes jumping on the BAYC bandwagon due to its exclusive membership perks and utilities. Owning a Bored Ape is a way to show off a status symbol due to the high price tag for each Ape, limited supply of 10,000 original ape minted and exclusive perks.
As Bored Ape owners, they are entitled to the following special privileges:
- Attend real life events or meet-ups offline with celebrity guests and performers
- Free NFT airdrops or future collections, such as Mutant Ape Yacht Club (MAYC) & Bored Ape Kennel Club (BAKC)
- Copyright license for commercial use
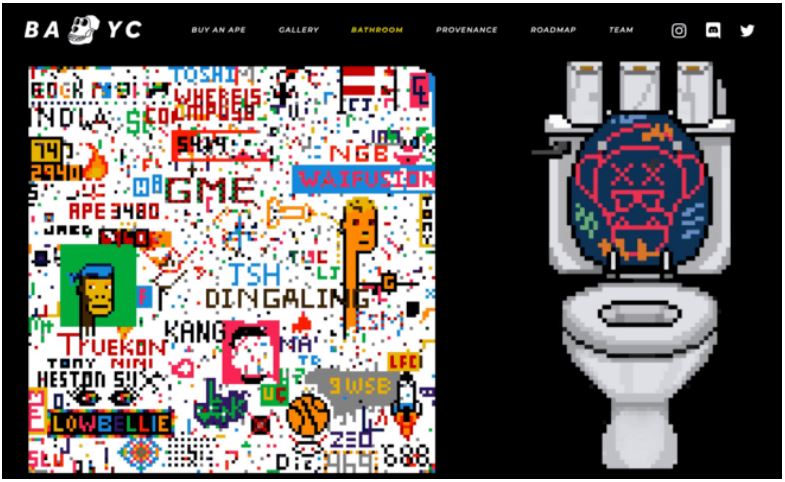
- Access to The Bathroom, a community drawing board where each owner has about 15 minute to paint a pixel to create collaborative art.
- Access to the game thematic universe, Apes vs Mutants mobile game
All perks and utilities offered to Ape owners were to keep their interests in the project, so that an exclusive community is built. Owning an ape is like owning a community pass, with lifetime membership to secret apes-only club, just like being in a billionaires club for the rich and famous.
Some even purchased Bored Ape as a potential investment asset as it has a finite supply of apes. When BAYC was first launched in April 2021, it cost a mint price of 0.08 ETH, which is about $200 that time (1 ETH convert to about $2700 range). As of Feb 2022, BAYC has a floor price of about $310,000 where the initial investors have profited about 1400x on this investment. Huat ah!
In addition, owning a highly prized and widely recognizable ape NFT is like owning a valuable art. The value of each ape is derived from subjective worth and demand, such as scarcity and uniqueness of the traits.
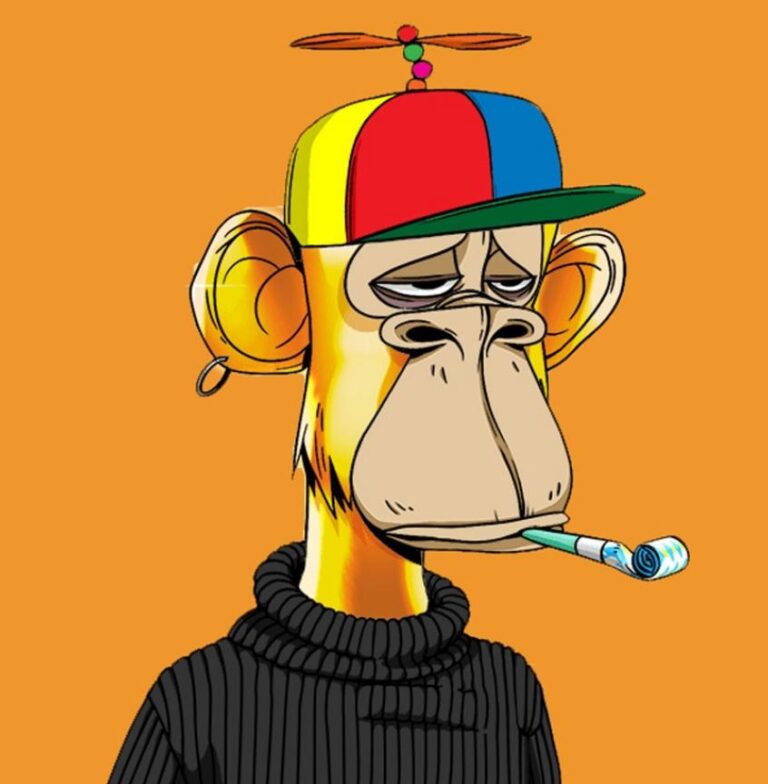

BAYC NFT #8817
The BAYC NFT #8817 was sold for $3.4 million on 27 Oct 2021, one of the most expensive BAYC NFT sold on Sotherby’s NFT platform metaverse. This is all because of its rare solid gold fur trait (only 46 apes out of 10,000 apes have this trait!)
Each BAYC apes have seven different traits, which use programmable graphics to randomly generate the traits:
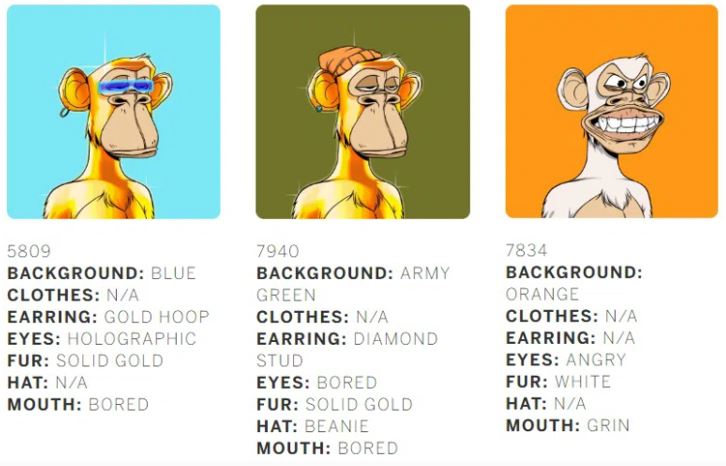
Different traits of bored apes
- Background
- Clothes
- Earring
- Eyes
- Fur
- Hat
- Mouth
Rank of the ape was determined by the rarity of its overall traits. An ape with rare attributes will be sold for a higher amount compared to an ape of common attributes.
For example, only 49 apes have bored dagger mouth out of 10,000 apes, like BAYC #8135. With all of the attributes added up, BAYC #8135 has a rarity score of 668.21 and lead it to Rank #1.
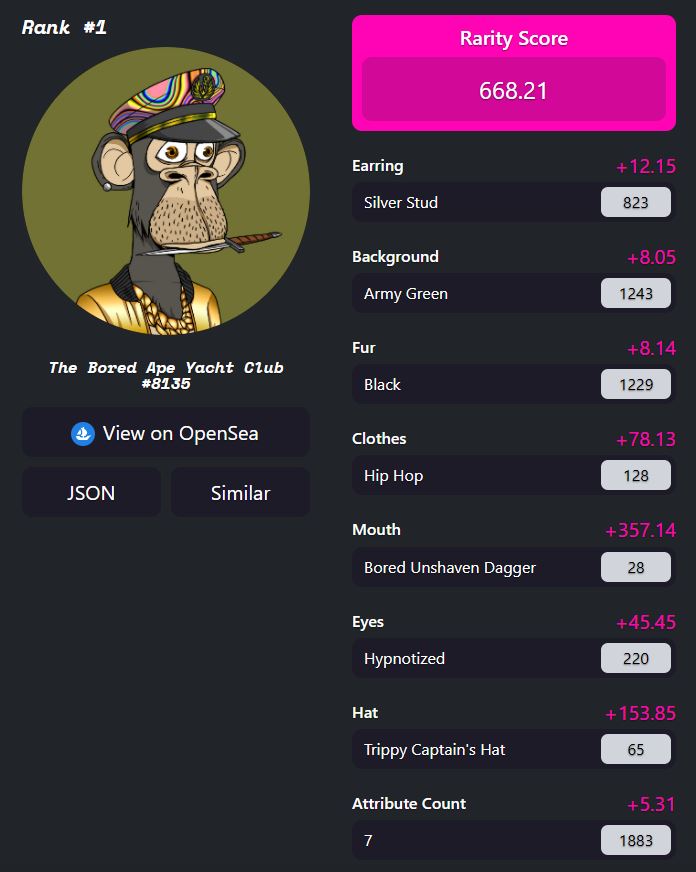
BAYC NFT #8135
RISK & BENEFITS OF NFTS
With all the sizzling sensations around NFTs, one is tempted to set foot into this shiny new arena and jump onto the NFT bandwagon to earn some extra bucks.
But, hold your horses!
We have also read news about various forms of crypto scams in the DeFi (decentralized finance) ecosystem and people have lost tons of money from it. Before investing any money into NFTs, we should also scrutinize the risks that may arise.
RISKS
The most famous crypto scams in NFT are rug pull. A rug pull is a malicious act where the crypto developers create interests about a new token with high potential value to entice investors to invest money in the project. Once investors have poured in enough money for the project, the developers will abandon a project and cashes out the funds raised. As a result, the investors are left holding an empty bag, an asset that holds no value.
Recent high-profile sales of NFTs also caught the attention of hackers where they hack into accounts and steal NFTs. Hackers take advantage of the loose security measures and use another valid account credentials to access the victims’ NFT accounts. They then sold off all the NFTs in the hacked account to purchase other NFTs and transferred the new NFTs to another account. The hacked account owner will no longer have any NFTs left in their account.
Some scammers even stole artworks of other artists, tokenize the artworks and upload them on NFT platforms for sale. Van Baarle, a Dutch digital artist and Qinni, a professional artist from Canada had their artworks turned into NFTs for sale, but none was being put up by them on the platforms.

As NFT metadata can be represented either On-chain or Off-chain, care should also be taken, especially for Off-chain NFTs. This is because Off-chain metadata is stored separately from the smart contract, in an off-chain storage system. Should there be a break down on the centralized server, there is possibility that the metadata is lost and the smart contract will only point to a broken link. It is not possible to rewrite the smart contract due to the non-fungible property of the NFTs.
Not forget to mention about the environmental concern that has been in heated debate about blockchain technology. To validate a transaction on the blockchain, miners will need to use “Proof of Work” method – a form of puzzle solving to verify transactions. This consumes huge amount of energy as they are using networks of computers to solve puzzles. In some blockchains, it can use as much electricity as the entire country of Libya to run the validation process.

Finally, people may be confused that when they buy an NFT, they should own the NFT. This statement is somewhat partly true and partly not true. Confusing, eh? To better explain this part, we will have to understand the definition of copyright.
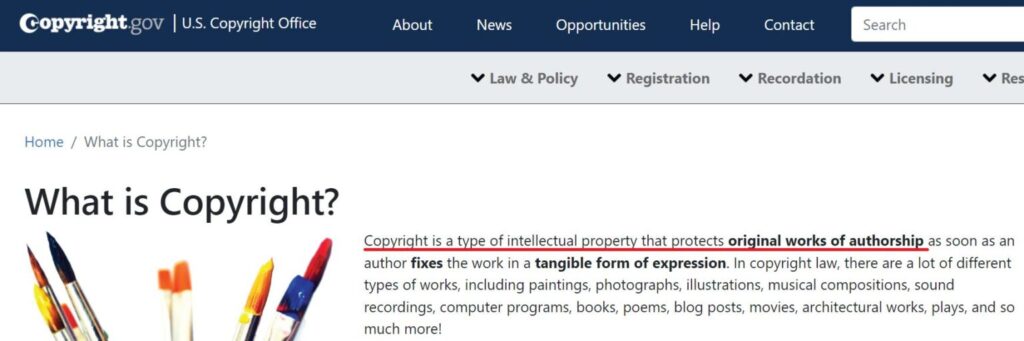
Based on the definition by US Copyright Office, copyright is referring to a type of intellectual property that protects the original works of creator as soon as the creator completes the work in a tangible form of expression. In short, the creator of the work is the copyright owner, and they can do anything they want with their creation.
When one purchase an NFT, they only own the NFT for personal use and not licensed to further produce or redistribute the NFT as the copyright belongs to the creator. An example of “NFT Terms” by Linkin Park’s lead vocalist, Mike Shinoda said it best:
“Only limited personal non-commercial use and resale rights in the NFT are granted and you have no right to license, commercially exploit, reproduce, distribute, prepare derivative works, publicly perform, or publicly display the NFT or the music or the artwork therein. All copyright and other rights are reserved and not granted.”
Example of “NFT Terms”
BENEFITS
Now with all the bad news aside, we will also look into the benefits and future potential usage of NFTs.
With the usage of smart contracts, NFTs can help to simplify the transactions without the involvement of the intermediaries or middlemen. If artists or celebrities plan to organize an event, they can easily sell the tickets to their fans directly via NFT and prevent frauds of e-ticket duplications.
In addition, with the metadata on NFTs, it can enable digital representation of physical assets such as licenses and legal documents to manage the identity of the owner. The irreplaceable nature of NFT only has one original copy available and can trace back to the rightful owner. It can help to proof the authenticity of the document, which is important, especially for file signatures and securing voting procedures.
CONCLUSION
Everything existed on two sides – the good and the bad, like the dynamite invention by Alfred Nobel whom he intended the explosives to be used in construction work but ended up being used in war for destructions.
This is the same with NFTs.
With the blockchain technology, NFTs can potentially be used as a digital representation of physical assets and proof of authenticity to minimize counterfeit problems. Nevertheless, blockchain technology and NFTs are still at its infant stage where there are lots of hiccups that will need to be ironed out before it can realize its full potential in the virtual world for years to come.
DISCLOSURE
The above article is for educational purposes only. Under no circumstances does any information provided in the article represent a recommendation to buy, sell or hold any stocks/asset. In no event shall ViA or any Author be liable to any viewers, guests or third party for any damages of any kind arising out of the use of any content shared here including, without limitation, use of such content outside of its intended purpose of investor education, and any investment losses, lost profits, lost opportunity, special, incidental, indirect, consequential or punitive damages resulting from such unintended use.