FTX is a cryptocurrency exchange and trading platform known for its derivatives trading. The sudden collapse of FTX in November 2022 plunged the cryptocurrency world into chaos.
Since 2022, we have seen a few collapses within the crypto space – LUNA, Terra, Three Arrow Capital (3AC), Voyager and Celsius. The series of crypto coins and lenders collapses had been dubbed as “Crypto Winter”.

Nevertheless, the most epic implosion in the crypto industry is now FTX, once the world’s third largest crypto exchange by volume and worth USD 32 billion at its peak. When news of FTX filed for Chapter 11 bankruptcy, it has sent grave repercussions throughout the crypto space. It is also mind boggling to know that what had led to the rapid downfall of world’s third largest crypto exchange within a mere few days.

In this article, we will unravel on what happened to FTX that led to its epic demise and the impact of its downfall.
WHAT IS FTX?
FTX, an abbreviation of “Futures Exchange” was a Bahamas-based cryptocurrency exchange which was founded by Sam Bankman-Fried (also known as SBF) and Gary Wang in May 2019.

Sam Bankman-Fried (SBF)
It was initially founded within Alameda Research, a trading firm that was also founded by SBF in 2017.
The cryptocurrency exchange offers crypto traders to buy & sell cryptocurrencies, trade various innovative products such as options and leveraged tokens on their platform. Investors can also park their money in accounts to earn higher interest rates than traditional banks.
FTX.com
FTX had attracted investment from some of the biggest names in the investment world including Sequoia Partners, the Ontario Teachers’ Pension Plan, SoftBank and the Singapore sovereign wealth fund, Temasek.
This had led to the rapid rise of FTX to international prominence and become one of the giants in the Crypto universe.
WHAT LED TO THE COLLAPSE OF FTX?
In early November, news that FTX was transferring customers’ deposit to Alameda Research was leaked on CoinDesk, a free crypto news service.
CEO of Binance, Changpeng Zhao (known as CZ) announced that they are selling their holdings of the FTX native coin, FTT on Nov. 6. This has led to the start of FTX downfall where many users of the crypto exchange also requested withdrawals of their money from the exchange, which triggered a classic “bank on the run”.
FTT is a native digital token created by FTX where it offered attractive perks to encourage people to use the token on the FTX platform for the services provided. People can buy and sell the FTT token, as if the tokens act like stock on the crypto platform.
As FTX was having liquidity issue to repay back the suddenly enormous amounts of withdrawals claims by their customers, they stopped processing the withdrawal requests on Nov. 8. To salvage the distress liquidity problem, the troubled exchange had reached out to various investors, including their once rival, Binance for help.
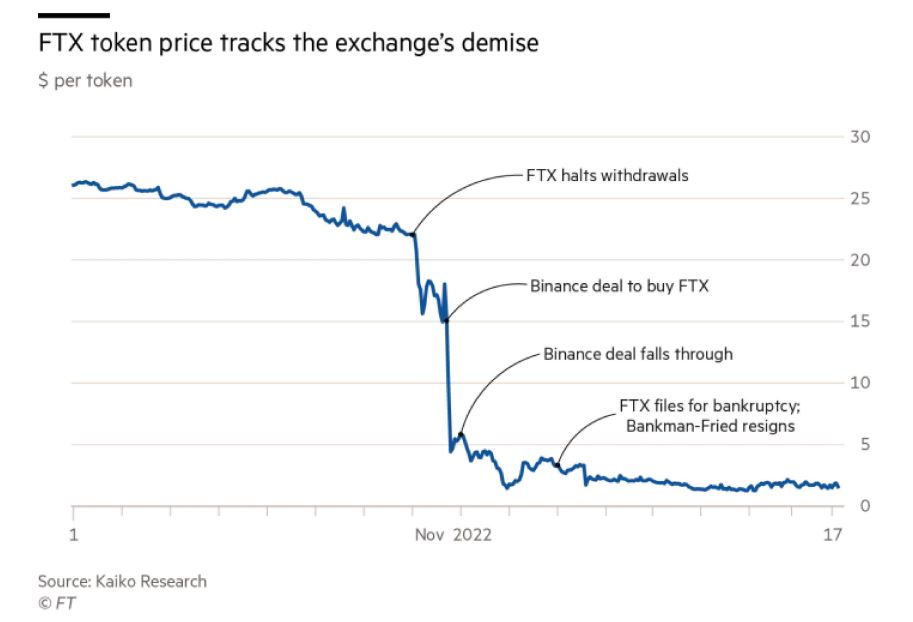
Binance initially agreed to acquire FTX, which provided a brief relief to various parties and investors. However, after Binance had performed due diligence on FTX’s finances, they decided not to proceed with the acquisition deal of FTX on Nov. 9.
On Nov. 11, FTX and Alameda Research had announced to file for bankruptcy, along with the resignation of SBF. This triggered a shockwave effect across the Crypto space, as FTX was once seen as the vanguard and protector of the new crypto economy where FTX purchased some of its struggling competitor, such as Voyager and Celsius during the start of the Crypto winter.
IMPACT OF THE COLLAPSE
After the collapse of FTX, many Venture Capital groups and retail investors that invested in FTX were seriously affected.

Various investment firms such as Singaporean sovereign wealth fund, Temasek had to write down a loss of investment that is worth USD 275 million (approximately 0.09% of its portfolio of SGD 403 billion as of 31 Mar 2022). Sequoia Capital also marked down its investment of over USD 210 million to zero. Whereas Softbank and Tiger Global each reported to lost USD 100 million and USD 38 million respectively.

Other than investment firms, the FTX’s meltdown contagion also affected other cryptocurrency firms and markets where huge losses are spreading throughout the crypto industry. Exchanges that did businesses with FTX (i.e. Galois Capital and Galaxy Digital) were reporting losses and crypto lender, BlockFi is preparing to file for bankruptcy. Severe declines in cryptocurrencies, such as BitCoin and Tether were reported when FTX’s collapse news was released in early November.
Individual retail investors who had invested a huge portion of their savings suffered the most in this latest crypto debacle, where they lost huge amounts of money and some had to file for bankruptcy after the collapse.
WHY PEOPLE INVESTED IN FTX, INCLUDING TEMASEK?
It is anyone’s best guess on why the world’s smartest and elite financials were being ‘fooled’ by SBF and decided to invest in FTX. However, from the latest news released on this incident, we may have some glimpses on the reasons why people invested in this latest crypto Ponzi scheme.
For Temasek, even though financial experts had conducted extensive due diligence on FTX in 2021, including interviewing people familiar with FTX, Temasek had “misplaced” its belief in FTX founder, SBF during their interactions with him. Temasek invested into FTX for the Blockchain ecosystem and its potential technology, but not direct investment into cryptocurrency speculations.
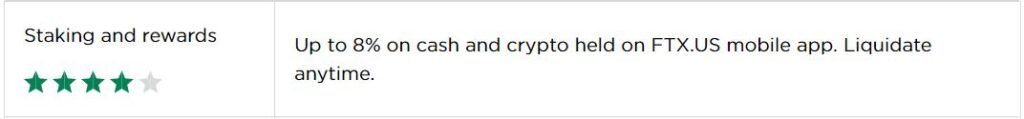
Whereas for individual retail investors, they thought that FTX was reliable and had investment backing of famous Venture Capital firms – Temasek, Sequoia Capital and Japan’s Softbank who had performed their due diligence on the crypto exchange. As a result, they decided to invest into FTX as the crypto exchange offered up to 8% in interest on both cash and crypto deposit on FTX.US mobile app before the collapse.
CONCLUSION – LEARNING LESSONS FROM FTX COLLAPSE
From the collapse of FTX, there are two main lessons that one can gather to become a better investor:
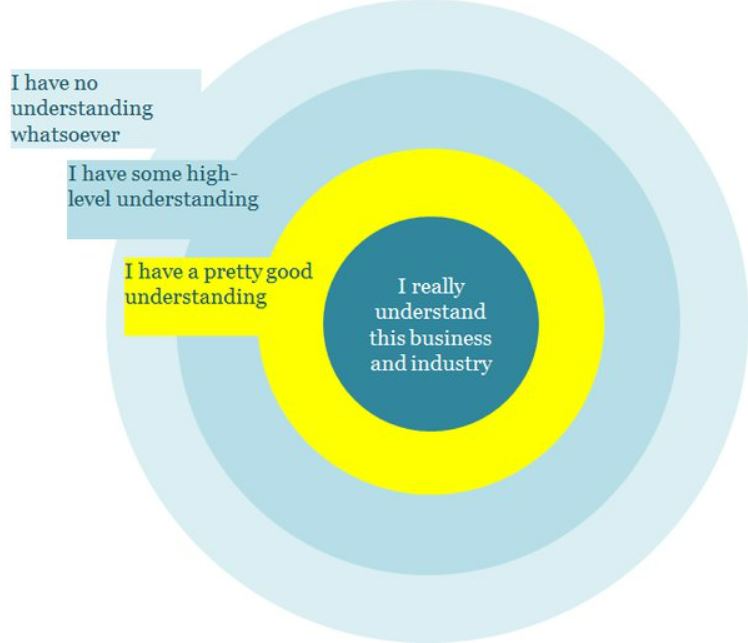
Circle of Competence – know what you are investing in.
Circle Of Competence
Before investing in any investment or crypto digital assets for this case, investors are strongly advised to perform investigations (known as due diligence) to determine if the investment is good and showed potential growth to be profitable.
However, if the investment does not make sense or hard to understand, it will be the best of interest for the investor to stay away from it to avoid losing money.
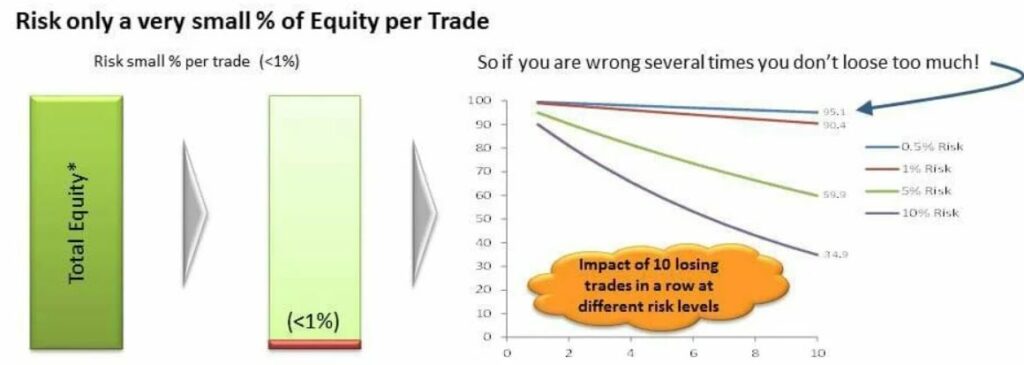
Position sizing (Risk management) – number of units invested in an investment, depends on the account size and risk tolerance of on investor.
Example of risk management via position sizing
Every investment has certain level of risks and investors need to determine their comfortable risk tolerance level besides perform due diligence before investing.
Although investing firms such as Temasek had reported a loss of USD 275 million, the size of the loss was only a mere 0.09% from its SGD 403 billion (estimated USD 292 billion) portfolio which is a lot less compared to retails investors who might have invested almost 100% of their money into FTX.
Even though the recent series of major crypto industry players meltdown had triggered a sense of fear among investors, the public are aware that investing can help to grow their money for a comfortable and worry-free retirement life.
When it comes to investing, the first thought came to a person’s mind is about buying or selling a company’s share on stock exchange. However, due to the uncertainty of the market conditions and unsure of how to determine a good & profitable company to invest in, this fear has stopped many people from taking action to invest.
DISCLOSURE
The above article is for educational purposes only. Under no circumstances does any information provided in the article represent a recommendation to buy, sell or hold any stocks/asset. In no event shall ViA or any Author be liable to any viewers, guests or third party for any damages of any kind arising out of the use of any content shared here including, without limitation, use of such content outside of its intended purpose of investor education, and any investment losses, lost profits, lost opportunity, special, incidental, indirect, consequential or punitive damages resulting from such unintended use.