HP Inc. (NYSE: HPQ) share price soared about 15% after the legendary investor Warren Buffett bought up to 11.5% stake of the company on 7th Apr 2022.
This peculiar move from Buffett has created electrifying headlines on various news channels and many investors are debating heatedly on the plausible reasons for Buffett to invest in HP Inc.
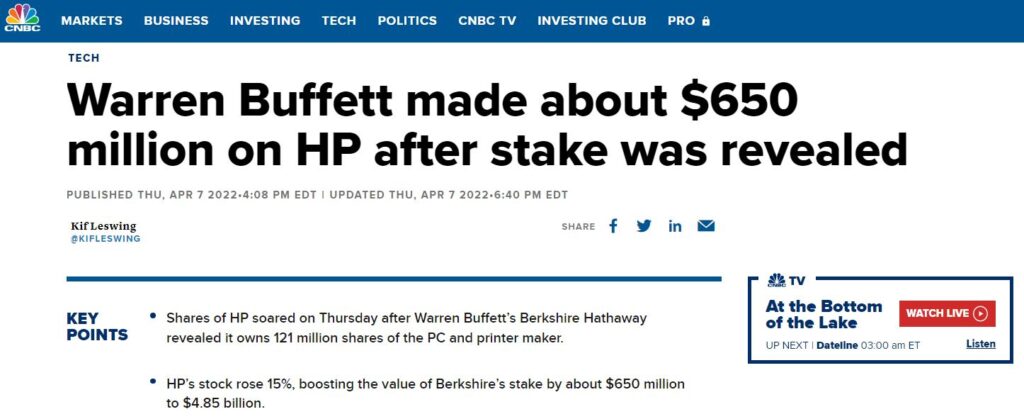
It is well known that Buffett tends to stay away from tech stocks. Nevertheless, this huge stake purchase has made people wonder what it is about HP Inc. that convinced the Oracle of Omaha to invest his money into this tech company stock.
Some articles reported that one of the reasons was because HP Inc. has been generating ample streams of free cash flow for the past few years and paying out dividends, which Buffett loves to collect.

In Feb 2022 shareholder letter, Buffett has shared some of his thoughts about Berkshire Hathaway’s selection criteria of what kind of businesses to invest in:

In this blog article, we will deep dive into HP Inc. and its fundamentals, while trying to determine the reasons for Buffett’s investment in the company!
COMPANY BACKGROUND
HP Inc. is a leading global provider of personal computing, imaging & printing products worldwide. The company also provides various business solutions for different industries and retailers.

It is the world’s second largest PC vendor by unit sales and market share after Lenovo as of January 2021, according to a research done by Canalys. Statista reported their research that HP Inc. has the largest market share for the printer segment in Mar 2021.
Their main target customers are individual consumers, small & medium-sized businesses (SMBs), and large enterprises (including customers in the government, health, and education sectors).
HP Inc.’s headquarter is based in Palo Alto, California, US. The company was formerly known as Hewlett-Packard Company (HPC), but was split into two independent companies in October 2015 into HP Inc. (NYSE: HPQ) and Hewlett-Packard Enterprise (NYSE: HPE).
HISTORY TIMELINE
Hewlett-Packard Company (HPC) was founded in 1939 by Bill Hewlett and David Packard in their garage, located at 367 Addison Avenue, Palo Alto to produce a line of electronic test and measurement equipment. The garage is now an official California Historical Landmark, known as the “Birthplace of Silicon Valley”.

The first financially successful product was an audio oscillator, Model 200B that was used in the audio production for Walt Disney’s animated film Fantasia in 1939.

During World War II, the company further expanded and manufactured various equipment, such as oscillators, voltmeter and analyzers that were used by the US army.
The timeline below simplifies the HPC’s historical milestones and innovative products launched throughout the years from the 1950s until the corporate split in 2015.
1957 – HPC launched an initial public offering (IPO) at $16.
1966 – Introduced the first computer, HP2116A and HP Labs that focused on R&D to innovate new technologies for the future.
1968 – First commercially available programmable desktop and scientific calculator, HP9100A was introduced.

1972 – First hand-held scientific calculator, HP35 that can fit inside a shirt pocket and HP 3000 minicomputer, used for commercial data processing were introduced.
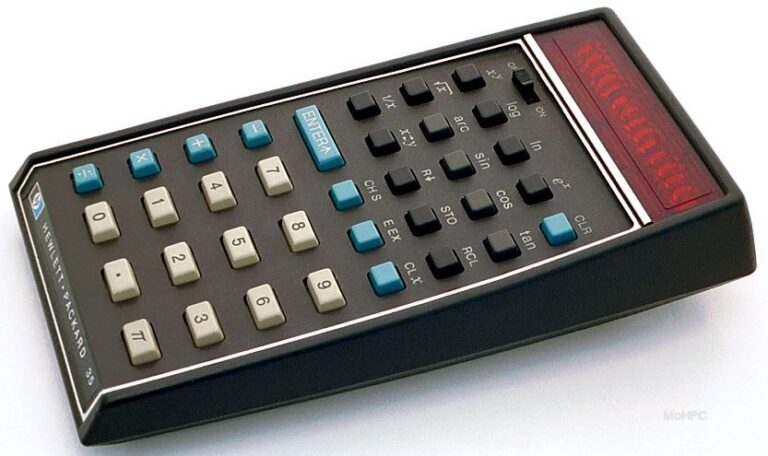

1980 – First personal computer, HP 85 with display, keyboard and printer integrated into one self-contained and portable unit was introduced.
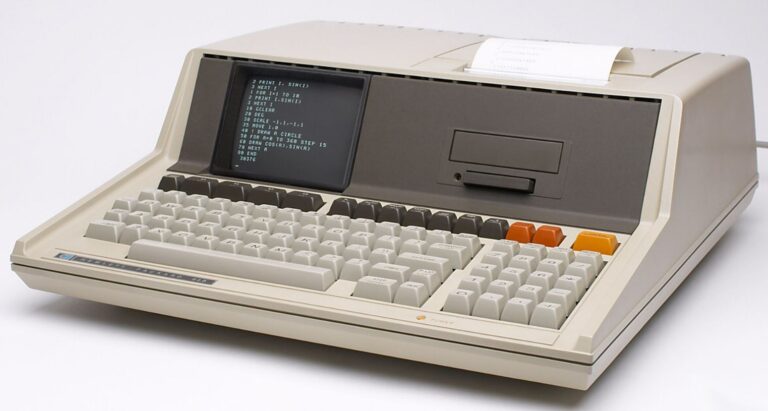

1984 – First desktop laserjet printer, 2686A that offered quality printing without the screeching sound of daisy-wheel printers was introduced.

1999 – To focus on the computers & imaging business, HPC spun off their electronic and bio-analytical measurement instruments into a separate company, Agilent Technologies.

2002 – HPC acquired Compaq to expand personal and enterprise computing products.

2015 – HPC was split into two independent companies – HP Inc. (NYSE: HPQ) & Hewlett Packard Enterprise (NYSE: HPE) in order to compete more effectively in the technology market.
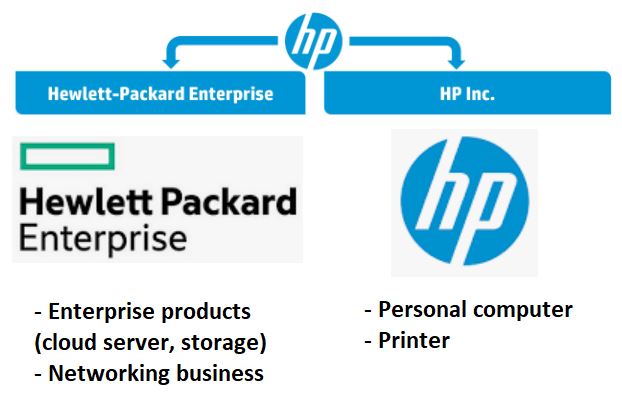
From 2015 onwards, HP Inc. carried on with HPC legacy and retained the pre-2015 stock price history until today.
Since 2016, HP Inc. has been expanding their personal computer and printer product offerings by launching PC gaming sub-brand, Omen. In 2017, they acquired Samsung’s Electronic printer division and Kingston’s gaming division, HyperX in 2021.
In 2019, HP Inc. made headlines as Xerox attempted to acquire HP Inc. but the attempted acquisition was called off in Mar 2020.
Products
HP Inc. sells personal computers (PCs) and printers (Print) in retail outlets and on their website.

The diagram below illustrates the various range of products and services offered by HP Inc. on their website:
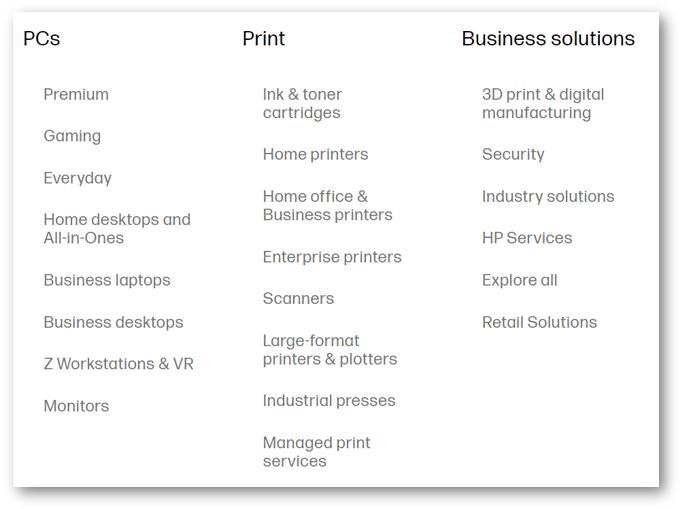
HP Inc. offers a broad range of PCs product portfolio from notebooks, desktops, workstations, thin clients, commercial mobility devices, retail point-of-sale systems, displays and peripherals, software, support, and services. The PC product offerings are categorized into two main usage categories:
- Commercial PC – optimized for large enterprises, public sectors (education, healthcare, etc) and small, medium businesses.
- Consumers PC – optimized for personal usage such as learning, entertainment and staying connected online.
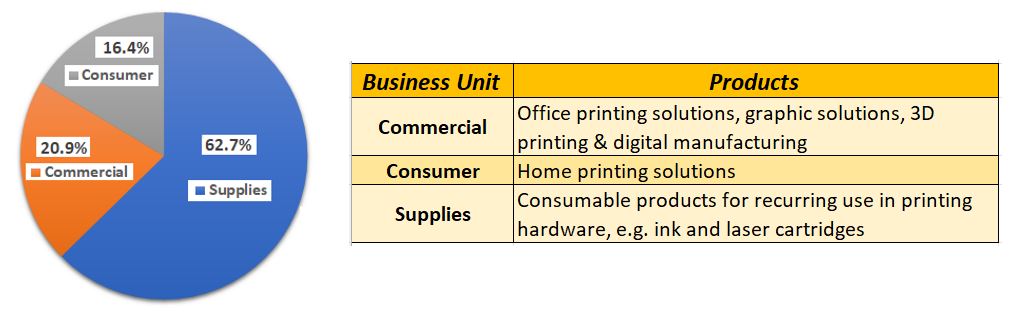
Print offers various printing hardware, supplies, printing & imaging solutions to their customers. The printing offerings can be categorized under four usage categories:
- Office printing solutions – Printing solutions for SMB & large enterprises
- Home printing solutions – Basic printing for personal & home business
- Graphic solutions – Large format, commercial printers
- 3D printing & digital manufacturing
Business Solutions is offered to help various industries to solve their specific business needs with the application of HP PCs and printers.

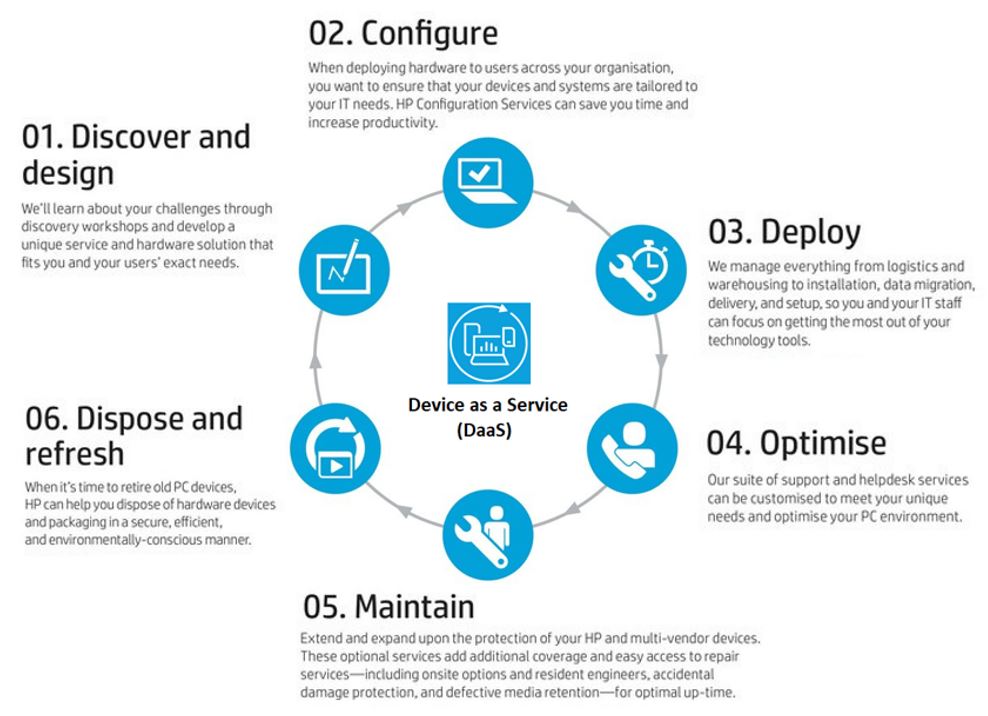
One example of the business solution offered is Device as a Service (DaaS), where HP Inc. provides a complete solution to help enterprises to better manage their IT assets. The diagram below illustrates how DaaS can help enterprises to optimize their IT assets usage lifecycle.
REVENUE GENERATION
HP Inc. has three reportable business segments:

Revenue was only generated from Personal Systems and Printing business segments.
Corporate Investments is set up to develop and innovate new technologies for computing & printing, such as desktop PC, inkjet printers and 3D graphics & printing. It is not directly involved in monetization of the projects during the research stage. Corporate Investments is comprised of:
- HP Labs
- Business incubation
- Investment projects
In 2021, HP Inc. generated a total of USD 63.5 billion net revenue worldwide from Personal Systems (68%) and Printing (32%) segments.
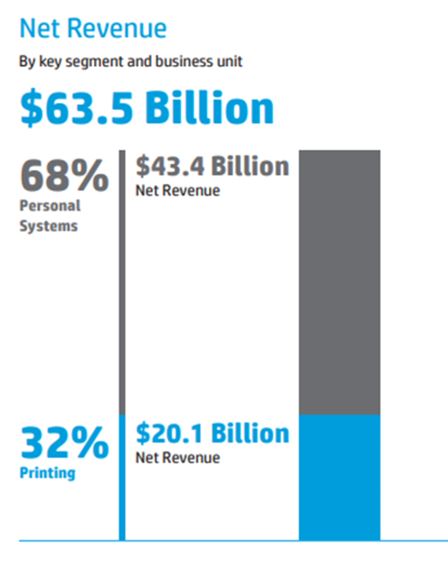
The pie charts below further detail the different business units that had generated revenue for the two business segments:
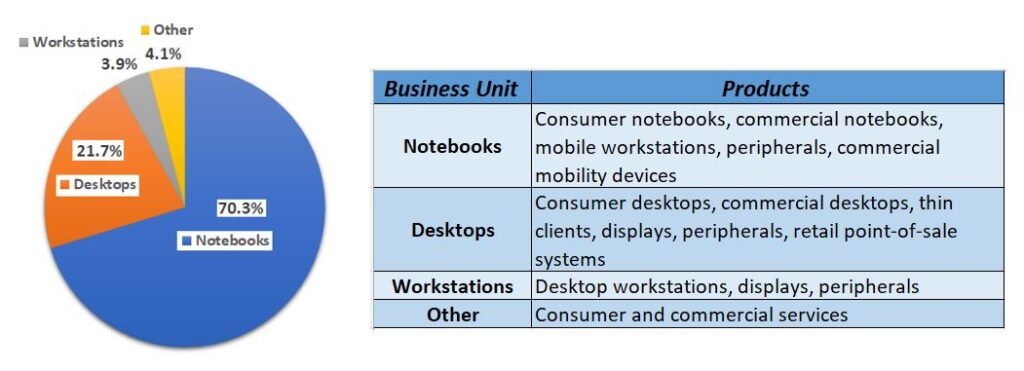
- Personal Systems has four business units to report on business performance and generated USD 43.4 billion revenue in 2021.
2. Printing has three business units to report on business performance and generated USD 20.1 billion revenue in 2021
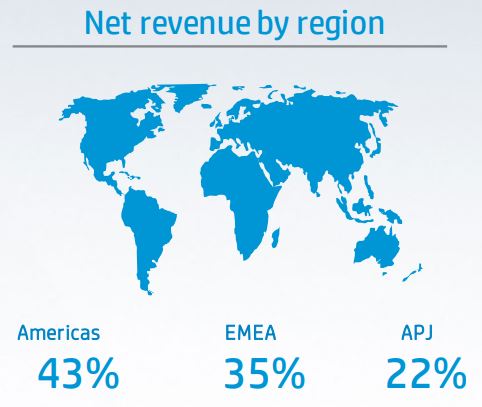
GEOGRAPHICAL REVENUE
When we look at the revenue generation from a geographical viewpoint, the Americas region contributed the largest portion, which is about 43% in 2021. Then followed by the Europe, Middle East & Africa (EMEA) region which contributed 35% and finally Asia Pacific & Japan (APJ) region, which contributed 22% of the revenue in 2021.
After going through the background and the revenue generations of HP Inc., it seems like this company has been doing well after the corporate split in 2015 . But do we really know if HP Inc. is a good and valuable company to invest in with potential growth?
FUTURE PLANS
HP Inc. has listed out three main pillars to drive the business for long-term profitable growth – Advance, Disrupt and Transform.
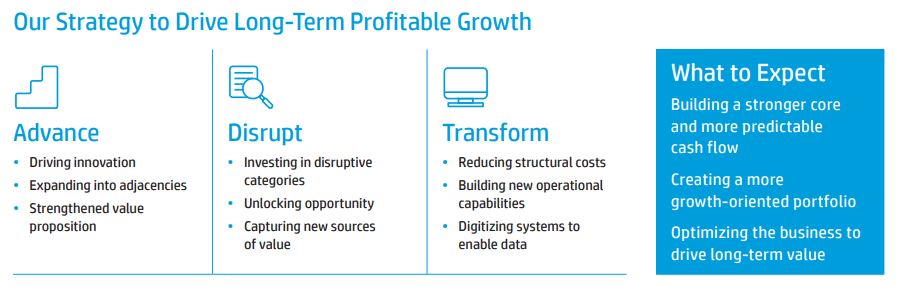
Under the Advance pillar, HP has strategized to strengthen their value proposition by expanding into adjacencies and innovating new products.
In Mar 2022, HP Inc. announced the acquisition of Poly to expand their peripheral product offerings and cater for the needs of future hybrid work environments.
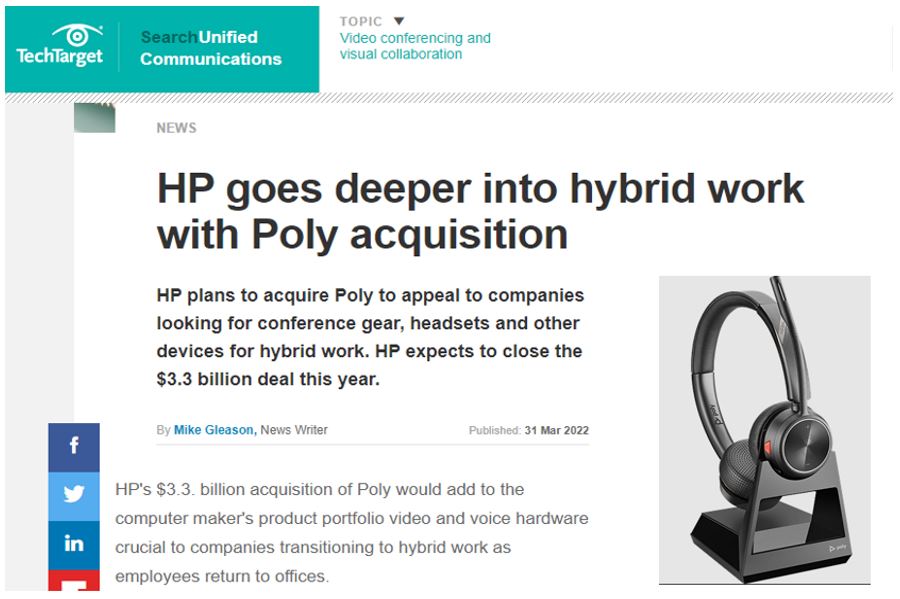
In addition, HP Inc. has also launched HP+, a breakthrough cloud-based printing ecosystem that further enhances the hybrid work environment.

For the Disrupt pillar, HP Inc. are investing in new and disruptive categories, such as 3D printing that can print more sustainable packaging and replace plastic packaging. They are also introducing instant ink subscription, changing the printing business to become subscription based.

In the Transform pillar, HP Inc. intends to transform the company to become more digital that helps to accelerate the company’s growth. In the 2021 Annual Report, CEO Enrique Lores shared that the company had invested in software and data science to better monitor their supply chain visibility. They are also sharing the data with channel partners to innovate and advance faster in the new business models.
ECONOMIC MOATS
Economic moat refers to the company’s ability to maintain its competitive advantages over competitors to protect the business market share and profits.
By Oct 31, 2021, HP Inc. reported that they owned more than 28,000 patents for their innovations and intellectual properties (IP). With patents, this enables HP to protect its innovation and technology from being copied by competitors or counterfeit products.
To protect the IP of the printer products, HP Inc. has introduced smart chip technology and initiated regular software updates on printers to ensure that original HP ink cartridges are used for HP printers.
In addition, HP Inc. has a wide distribution network worldwide where consumers can easily purchase HP products from retail outlets or on their website. Some countries offered next business day delivery for online purchase, such as Singapore.

As HP Inc. is offering business solutions to enterprises, such as DaaS for efficient IT assets management, it can be a potential high switching cost for enterprises should they wish to change to another vendor to manage their IT assets.

COMPETITORS
As HP Inc. is focusing on the personal computer and printer market, we are looking into these two segments to find out who are the competitors and how much of the market share that HP Inc. has taken for each segment.
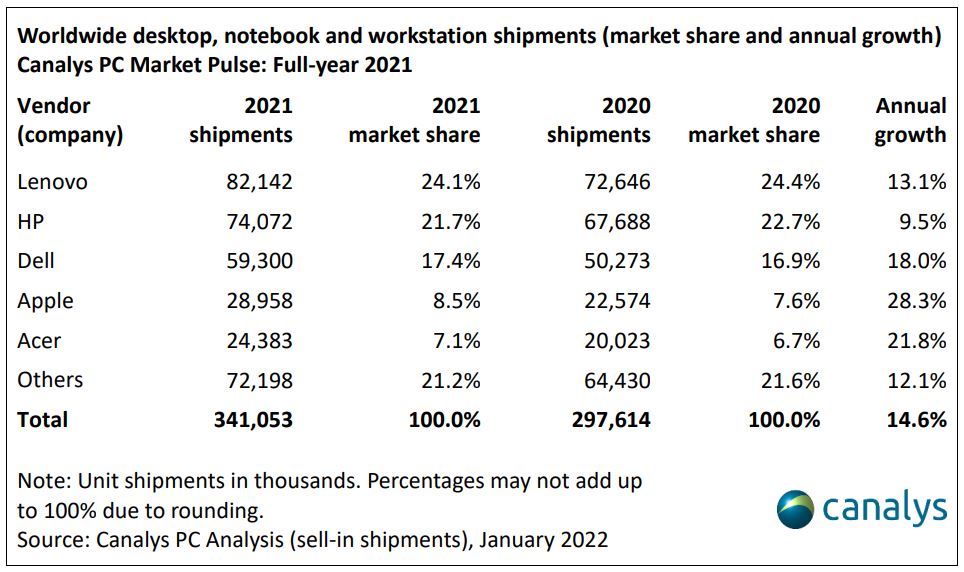
A research done by Canalys in 2022 reported that Lenovo took up the largest market share of PC shipments worldwide in 2021, at 24.1%. HP Inc. comes in second place, taking up 21.7% of market share, followed by Dell (17.4%), Apple (8.5%), Acer (7.1%) and other brands (21.2%).
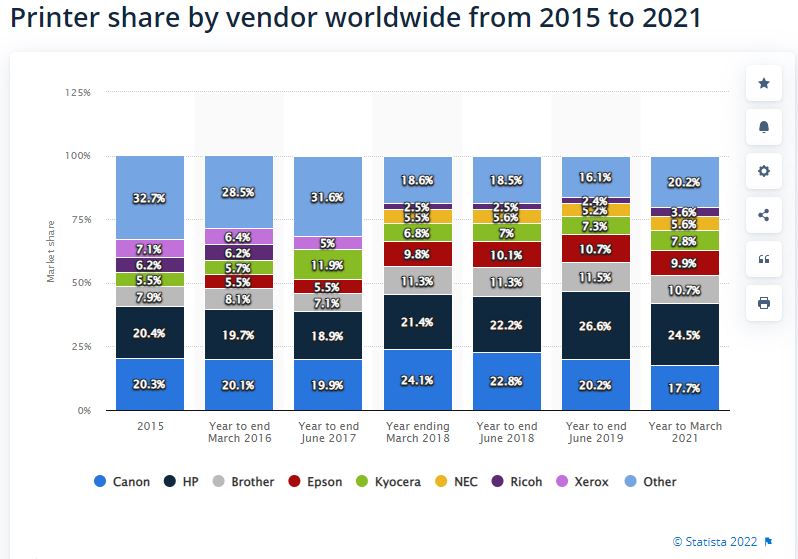
For the printer segment, Statista reported that HP Inc. is leading the industry by taking 24.5% of the market share in 2021. Second place was taken by Canon (17.7%), then Brother (10.7%), Epson (9.9%), and Kyocera (7.8%). Other printer brands took up the remaining 29.4% of the market share.
From these two statistical data, HP Inc. ranked among the largest printer shipments and second largest PC shipments in 2021 which suggested that HP brand is still a favoured go-to PC & printer brand for consumers.
From the exciting future plans that HP Inc. has announced, they have been working hard to generate different sources of revenue generations and the company also intends to fortify its industry leading position with its innovative products!
Nevertheless, it is also important for us to understand the company’s financial statements to better analyze the company and determine if it is a good company to invest our money.
FINANCIALS
For the financial section, we will be looking at the financial results after 2016 as HPC was officially split into two companies in November 2015. Prior to 2016, the HPC annual report still reported the financial results for both HP Inc. (HPQ) and Hewlett-Packard Enterprise (HPE).
In this revenue chart, there was a huge drop in 2014 because this chart shows only the revenue generated from the PC and Printer division (future HPQ). Revenue from the enterprise products division (future HPE) was not reported in this chart (The corporate split was announced in 2014 but the official split was in Nov 2015).
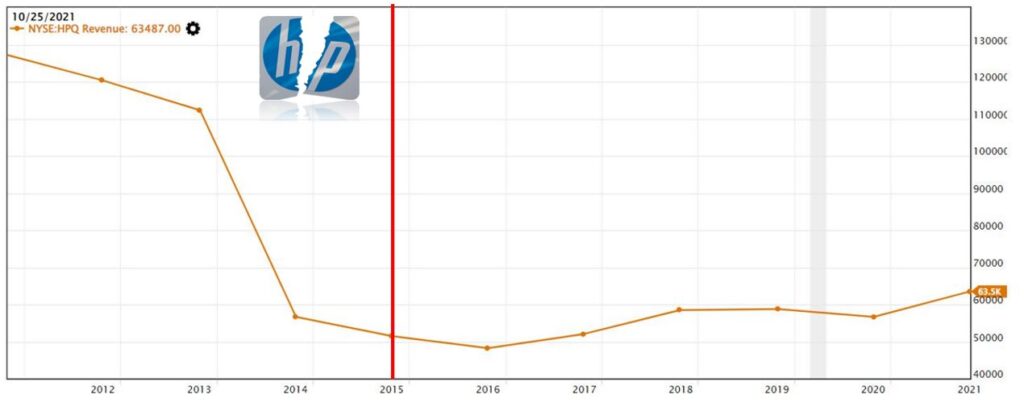
Since 2016, the revenue has been slowly increasing but there was a drop in revenue in 2020. The revenue dropped in 2020 was due to demand weakness for desktops and commercial printing hardware as most workers were working from home during the COVID-19 pandemic.
The revenue increase in 2021 was due to strong demand for Notebooks as most workers are still working from home.
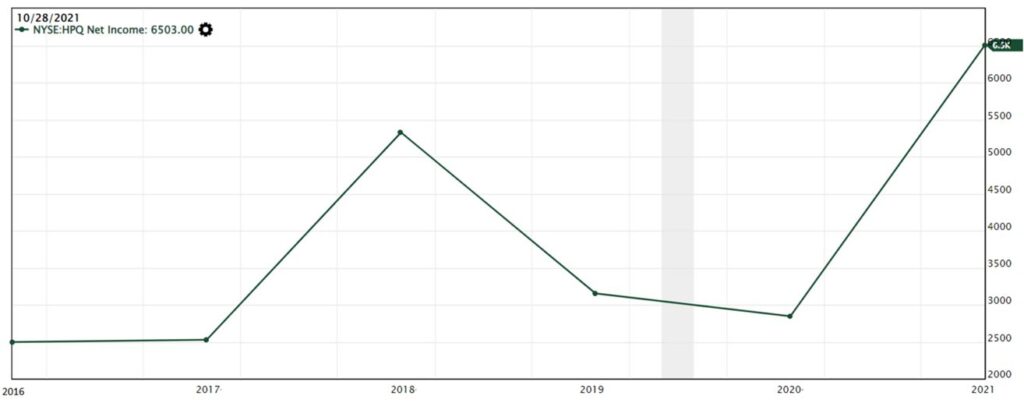
Next, we look into the company’s net income, which is the profit obtained after deducting the cost of goods sold (COGS) and operating expenses from the total revenue.
For the net income, we noticed that there was a spike up in 2018. Further investigation in the annual reports revealed that 2018 has tax rebates due to tax reform which increased the net income.
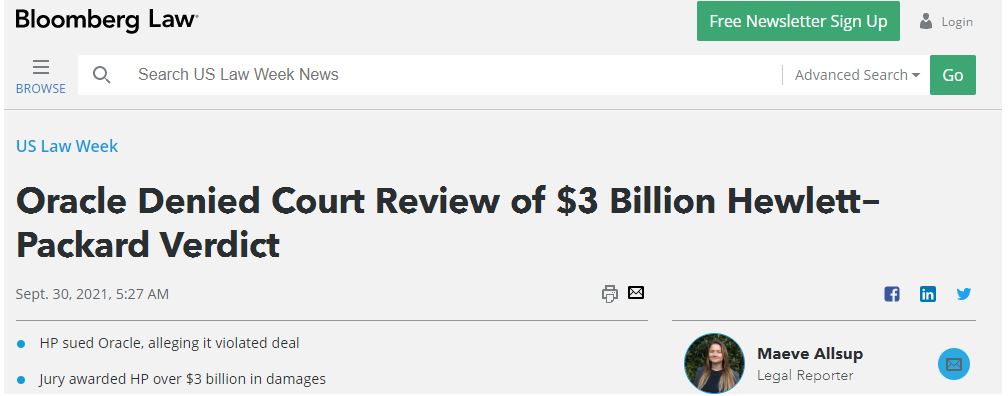
The sudden surge in 2021’s net income was due to a one-time litigation proceeds received from Oracle as HP sued Oracle for breaching the agreement by ending product sales for HP platform.
We also checked on HP Inc.’s earnings per share (EPS) as this financial metric indicates how much profit the company can generate for every share that the investor had purchased.
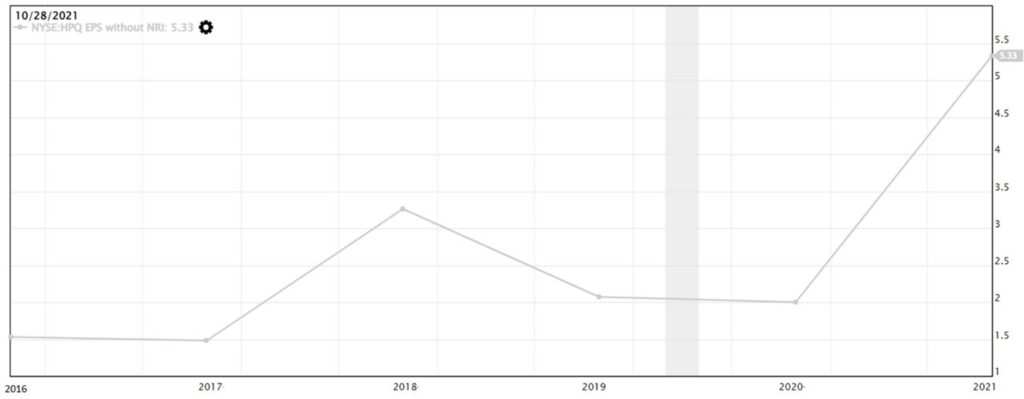
In the earnings per share (EPS) chart, we noticed that the similar trend pattern as net income was observed. Based on the mathematical formula below, if the EPS is $5, this means that for every share that was being purchased, the company can generate $5 of profit (net income).

If we were to remove the tax rebate in 2018 and one-time litigation proceeds from the Oracle case in 2021, the newly adjusted Net Income & EPS chart will look like this:
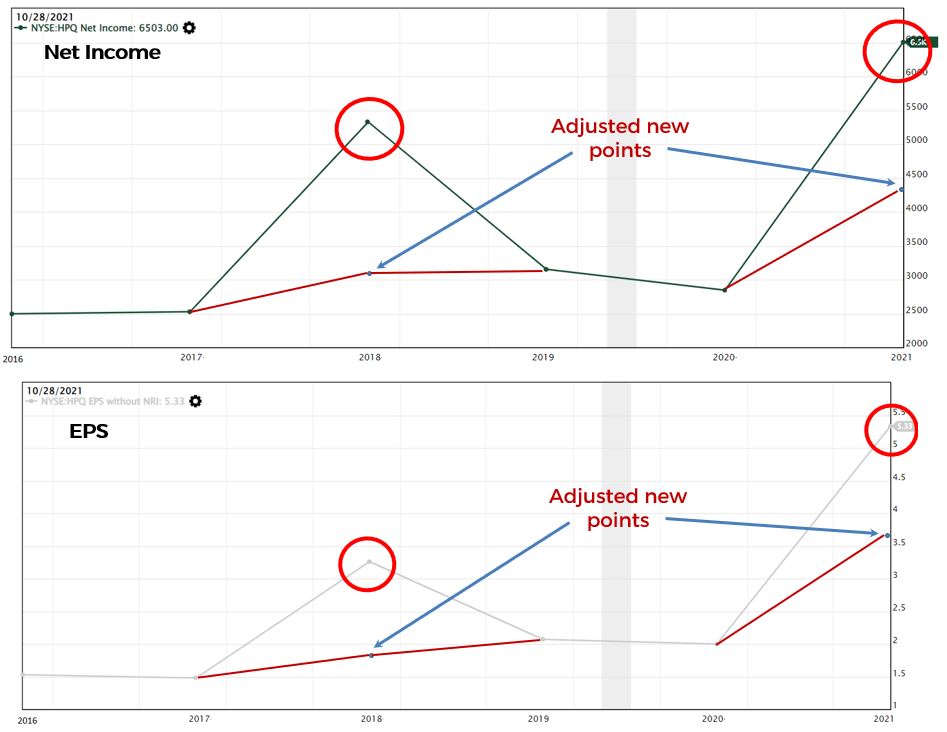
The overall trends for both charts are still on an increasing trend after adjustments which is a good sign that the company can generate profits. The drop in 2020 for the adjusted Net Income chart was due to reduction of revenue (refer to the Revenue chart above).
Follow up, we will look into the company’s Free Cash Flow (FCF). FCF refers to the cash left over after the company deducted the Capital Expenditure (CapEx) from the Operating Cash Flow. Operating Cash Flow is the cash flow generated from normal business activities and CapEx is the expense used to purchase assets that will last more than twelve months.
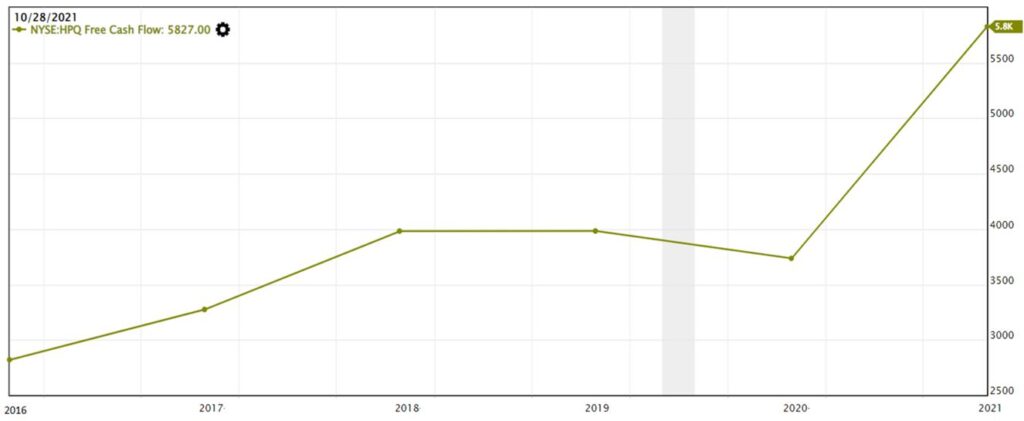
The overall trend of FCF is increasing, except a drop of about 6.2% in year 2020. This was because there was a reduction in Revenue and Net Income during that year which also affected the operating cash flow generated from the normal business operations.
Next, we investigate into the company’s balance sheet to determine what assets does the company owns and any debts that the company owes.
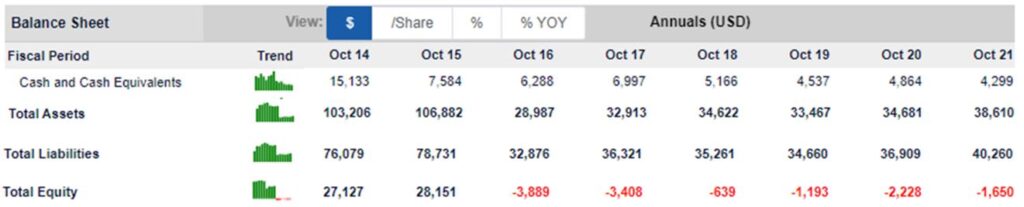
From the Balance Sheet, we observed that since HP Inc. has negative equity since 2016. The 2016 annual report revealed that the negative equity was due to the official separation of Hewlett-Packard Enterprise that led to the reduction of shareholder’s equity of $37.2 billion and cash dividend payout of $858 million for that year.
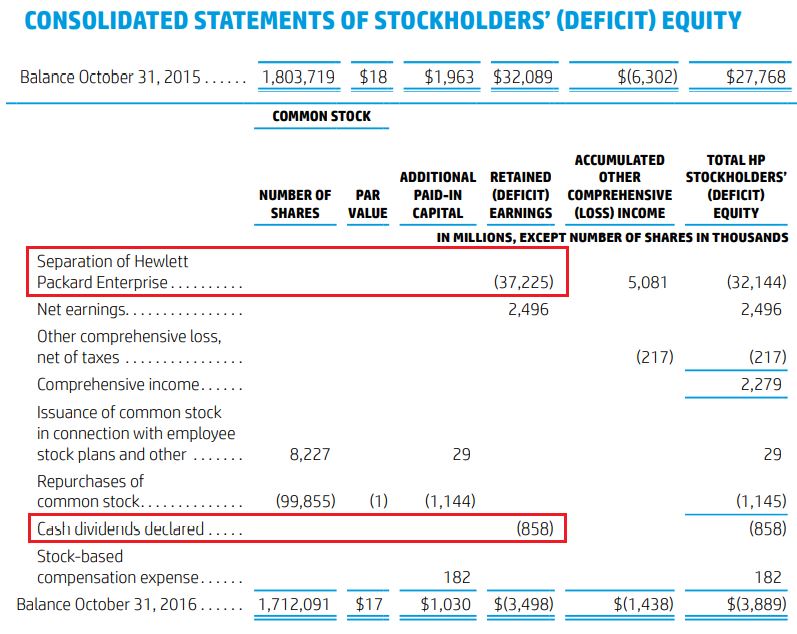
Data source: 2016 Annual Report
Even though the shareholder’s equity is currently in the red, if HP Inc. remains profitable for the subsequent years, we may expect to see this number to become positive in near future.
We also looked into HP Inc’s Debt/Asset ratio which depicts how much debt did the company take on to finance its assets and fuels the company’s growth.
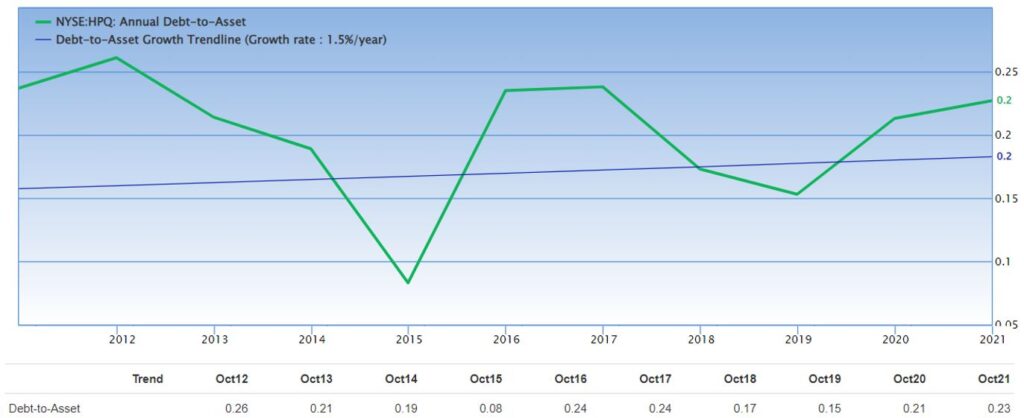
According to Value Investing Methodology, if the Debt/Asset ratio is less than 0.5, it implies that the company is not over-leveraged or take up too much debt to grow the company’s assets. In simpler terms, it means that for every $100 of asset, the company takes up no more than $50 of debt to grow the company.
From the chart, we observed that HP Inc. has been managing their Debt/Asset ratio between 0.15-0.24 since 2016, which is below 0.5. This implies that the company has not taken up too much debt to grow the company.
To determine the management’s efficiency in running the company and generating profits, we also looked into Return on Assets (ROA). ROA measures how well is the company using its assets to generate profits and the mathematical formula for ROA is Net Income divided by Total Assets. According to Value Investing Methodology, if the ROA of a company is above 7%, it implies that for $100 of assets, the company is able to generate $7 of profit.
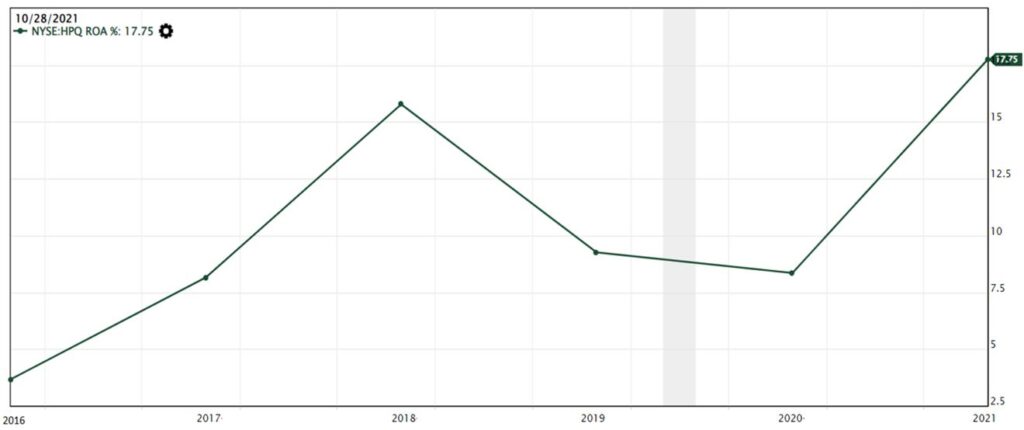
From the ROA chart, we observed that since 2017, the ROA has been above $7 and this implies that the management is effective in using the company’s assets to generate profits.
POTENTIALS RISKS
Now we will look into any potential risks and concerns that HP Inc. may have and could potentially derail investors’ investment in the company.
As the Covid-19 pandemic is slowly dwindling and the imposed restrictions are slowly loosening, more workers will be returning back to office to work. As there might be lesser workers to be working from home, the demand for Notebooks may be impacted and sales will slow down. Lower volume sales will reduce the company’s revenue, as this was seen in 2020 when the commercial desktops and commercial printer sales dropped at the start of the Covid-19 pandemic.
In an article by Forbes, the author mentioned that HP has no exclusive moats to maintain its competitive advantages over competitors, especially for PC. As there are many PC manufacturers worldwide that can produce PCs with newer technology features but at a cheaper price, consumers have a myriad of PC choices to choose from. Thus, HP Inc. will have a stiff competition with the other manufacturers.

In addition, HP products also lack universal appeal or status symbol that will attract fans, like Apple products. As a result, there is a possibility that the product unit sales may drop if the competitors have more attractive products and features than HP.
If the consumers do not like certain aspects of the HP products, they may change to other brands and thus reduce the unit sales of HP products. This was observed when consumers gave feedback that the original HP ink cartridges were expensive and they used cheaper remanufactured ink cartridges. However, after software updates of the HP printers, the printers can no longer use the remanufactured cartridges. The consumers were unhappy that they were being ‘forced’ to use original cartridges and considered not purchasing HP products in the future.
CONCLUSION
After investigating this company, HP Inc. has plans to maintain their market leader position in PC & Printer segments with various exciting long-term growth plans and ground-breaking innovations.
Nevertheless, the lack of exclusive moats or addicting appeal for HP products may not motivate investors to put their hard-earned money into the company as one might still be concerned if the market leader position can be uphold in near future. This was observed when Lenovo dethroned HP market leader position in 2013 in terms of overall PC shipments.
However, should the company focus on continuing to create reliable and high-quality products, where the HP brand was well-known for in the past, consumers may still purchase the products because of the brand.
DISCLOSURE
The above article is for educational purposes only. Under no circumstances does any information provided in the article represent a recommendation to buy, sell or hold any stocks/asset. In no event shall ViA or any Author be liable to any viewers, guests or third party for any damages of any kind arising out of the use of any content shared here including, without limitation, use of such content outside of its intended purpose of investor education, and any investment losses, lost profits, lost opportunity, special, incidental, indirect, consequential or punitive damages resulting from such unintended use.