US President Joe Biden’s signing of the CHIPS Act in Aug 2022 has drawn attention worldwide, putting the semiconductor industry in the limelight and generated enthusiastic anticipation of the industry’s future growth on the US soil.

As most of our smartphones, PCs and future technologies such as Artificial Intelligence and 5G need semiconductor to operate, the chip has become an important part in our technological devices. Without it, all of these devices cannot function and our modern-day world may come to a screeching stop.
The recent visit of the US House Speaker Nancy Pelosi in early Aug to Taiwan has triggered chip shortage concerns as the tension between China and Taiwan escalated. Currently, the world’s largest producer of semiconductor is currently located in Taiwan.

In this blog, we will be exploring one of the world’s largest chip makers in Taiwan – TSMC and find out if this is a good company to invest in during these peril times.
COMPANY BACKGROUND OF TSMC
Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company, Limited (TSMC) was founded by Dr. Morris Chang in 1987 as the world’s first pure-play foundry business.

Dr Morris Chang
They only focus on manufacturing semiconductor chips for their customers and did not manufacture the chips under the company’s name.
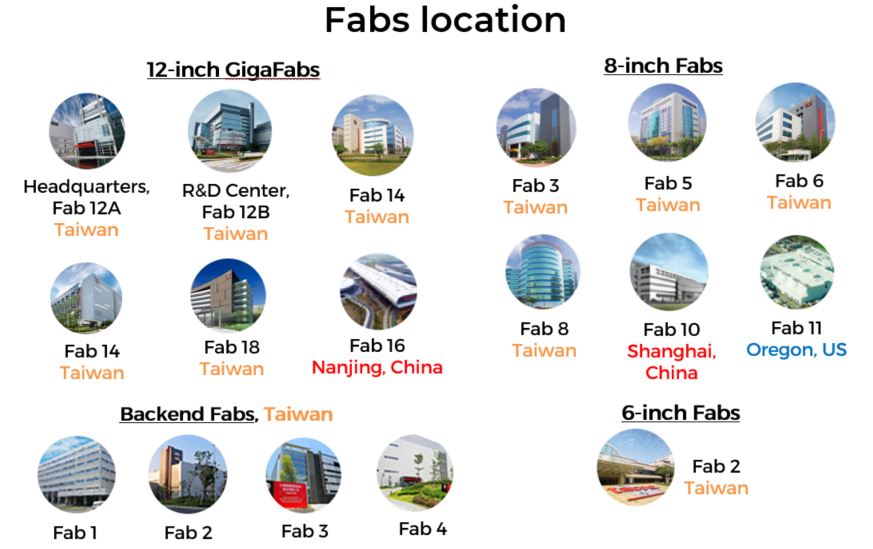
TSMC’s headquarters is in Hsinchu Science Park, Taiwan. They have several production sites, known as fabs located in Taiwan, US, and China. There are:
- Six 12-inch wafer fabs
- Six 8-inch wafer fabs
- One 6-inch wafer fabs
- Four backend fabs (for testing and assembly of the completed chips)
In 2021, they have manufactured a total of 12,302 different products by using 291 distinct process technologies (node) for 535 customers worldwide. We will further explore TSMC’s customers in the Economic Moats section below.
PRODUCTS
TSMC mainly manufacture semiconductor chips from silicon wafer as approximately 90% of the revenue generated in 2021 was from semiconductor chips sales.

Worker inspecting silicon wafer
The chips manufactured are being used in 5 major markets:
- Smartphones
- High Performance Computing (HPC)
- Internet of Things (IoT)
- Automotive
- Digital Consumer Electronics (DCE)
The market share for each of the major markets will be further discussed in upcoming Revenue Generation section.
CHIP MANUFACTURING PROCESS
As TSMC only focuses on fabricating semiconductor chips, they can set up state of the art chip manufacturing process. The diagram below shows the simplified version of the semiconductor manufacturing process.
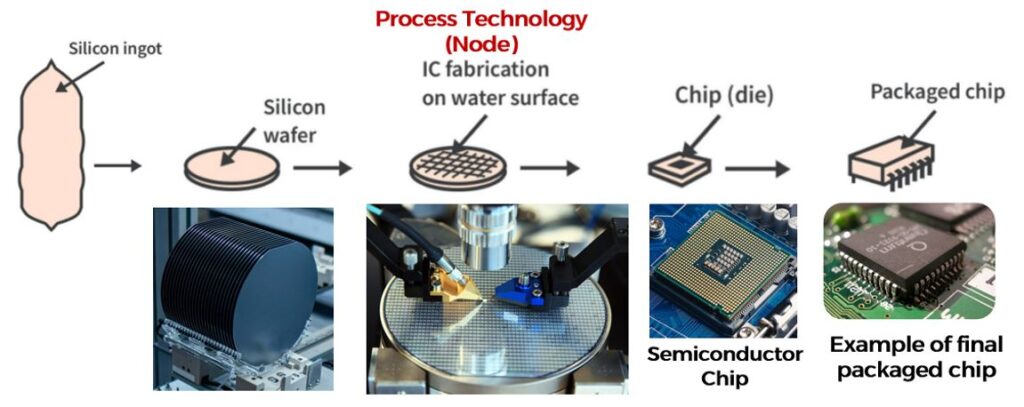
The raw material – silica is first being mold into silicon ingot before they are being sliced into wafer plates. The silicon wafer will then undergo various chemical process so that the wafer surface is ready for the next step process – to fabricate the chip circuit design on the silicon wafer.
The chip will be fabricated according to the dimension and circuitry that was designed by chip designer companies. This fabrication process is known as process technology or node. The node is the manufacturing process and design rules that chip makers used to fabricate the circuit design of chips onto the wafer plates. This process is known as photolithography.
The diagram below illustrates the process of how the chip circuit design is being imprinted onto the silicon wafer.
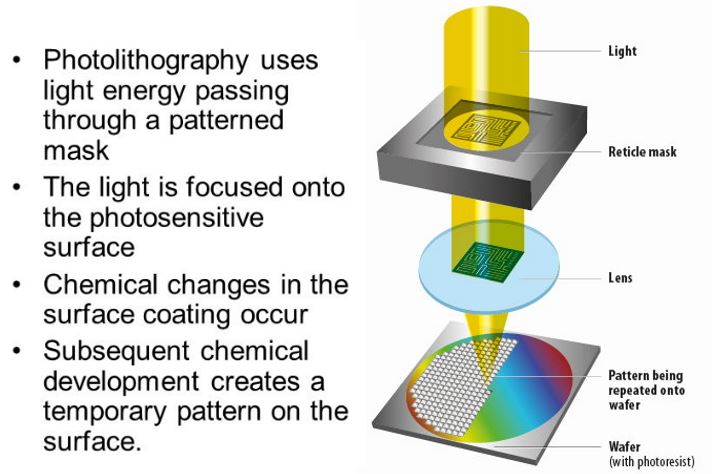
The smaller the node, the more advanced technology is required as they will be using lower wavelength of UV light to imprint the circuitry design onto smaller chips while adding in more transistors onto it. With more transistors on the chip, the more powerful and energy efficient the chip becomes.
Once the design has been imprinted, the chips will be cut into smaller pieces before being packaged and assembled into final products. The finalized product will have to undergo testing to make sure that the chips are working well and within specification before being released to their customers.
REVENUE GENERATION
In 2021, TSMC generated a total revenue of USD 56.82 billion. About 88.5% was generated from wafer production and 11.5% was generated from Others.
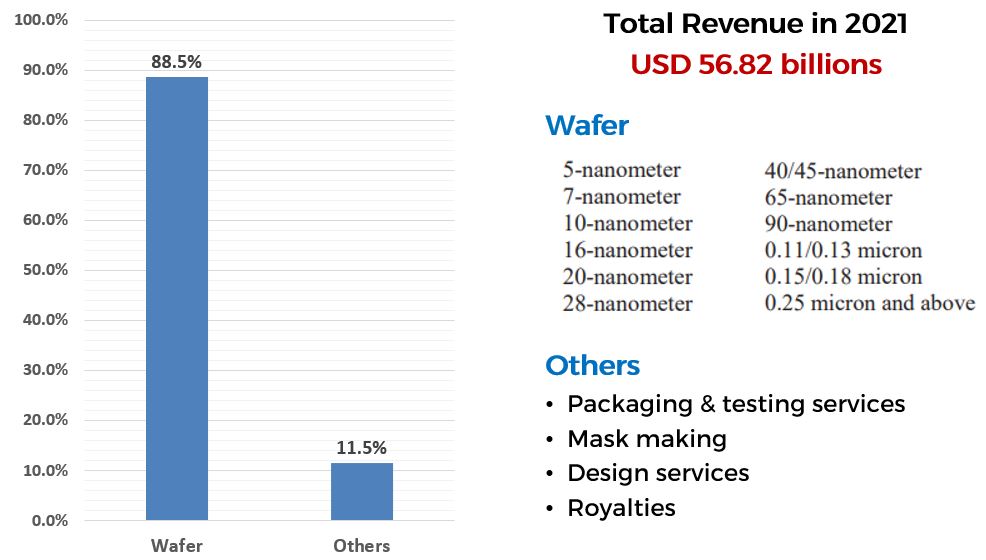
TSMC 2021 Annual Report
We also further analyze the revenue source from three different aspects – by process technology, application platform and geographical region.
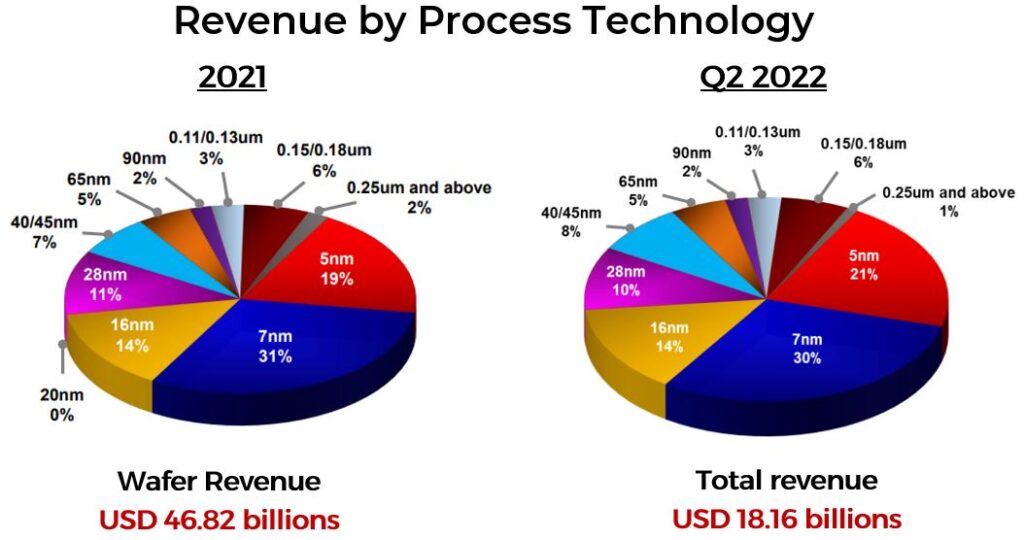
TSMC Quarterly Report
Although TSMC manufacture other chip sizes, most of the revenue is generated from advanced microchips – 7nm & 5nm, which made up almost 50% of the revenue earned in 2021 and Q2 2022. 7nm is the highest grossing process technology for both 2021 (31%) and Q2 2022 (30%), followed by 5nm, which contributed 19% in 2021 and 21% in Q2 2022.
(Q2 2022 was reported in Total Revenue as the breakdown of the revenue was not reported in TSMC’s quarterly report)
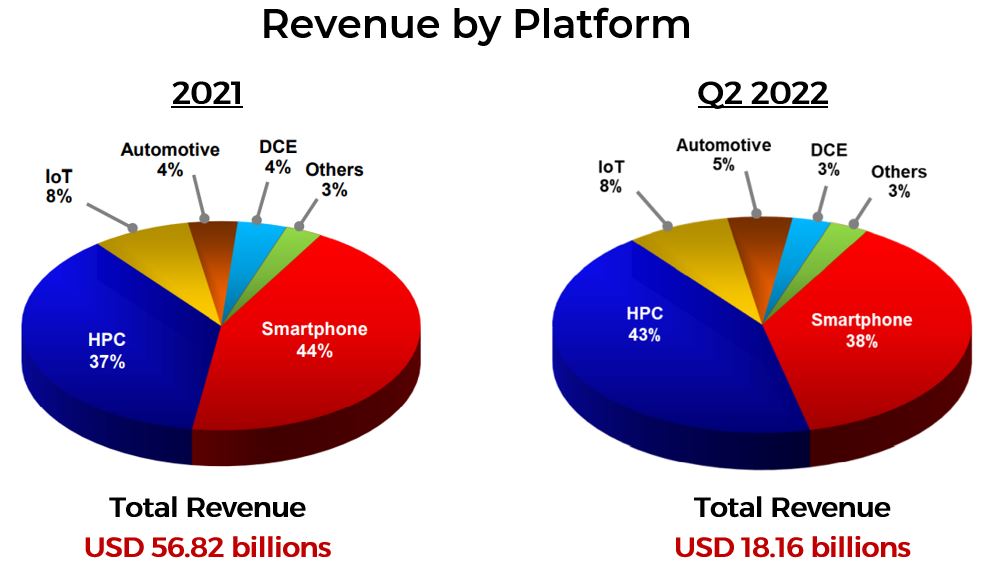
TSMC Quarterly Report
For the application platform, 44% of the chips are generated from the Smartphone platform, followed by HPC (37%). However, HPC generated the most revenue (43%) compared to Smartphone sales (38%) in Q2 2022.
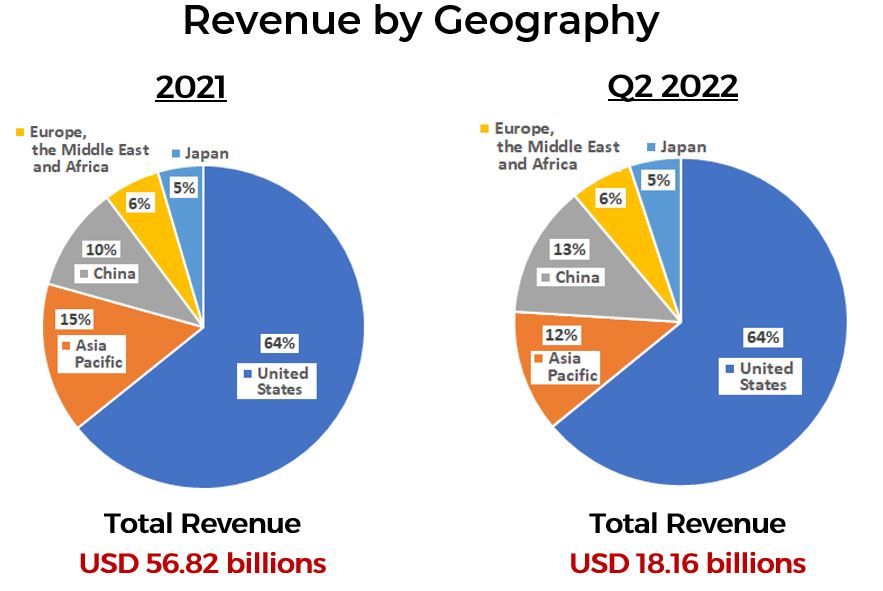
TSMC Quarterly Report
From the perspective of geographical region, majority of the chips manufactured by TSMC was being sold to the United States (64%) for both 2021 and Q2 2022. Another interesting thing to note of is that in 2021, about 10% of TSMC’s revenue is from China, but this number has increased to 13% in Q2 2022.
After going through TSMC’s company background and the revenue generations, although the company only produces semiconductor chips but it is one of the largest advanced microchip (5nm & 7nm) producers in the world!
FUTURE POTENTIAL
TSMC has made plans to expand their production capacity overseas, which is in US and Japan.
In 2020, TSMC has announced to set up a 5nm chip production site in Arizona, Phoenix, US. The construction has started in 2021 and expected the plant to be fully operational in 2024.
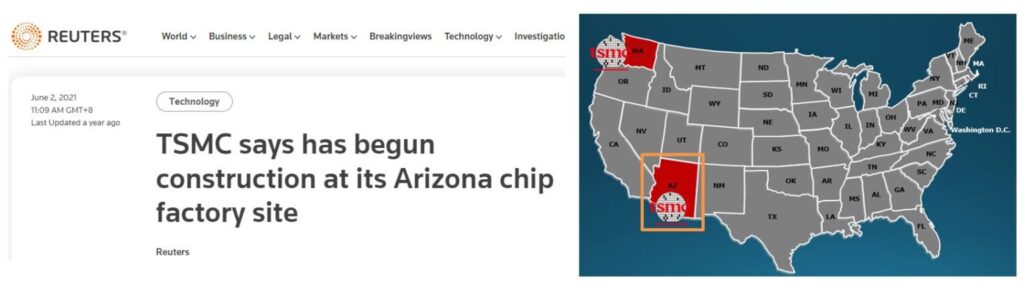
For Japan, TSMC has announced to set up a 12-inch wafer manufacturing site in Kumamoto, Japan. They expect the site to be in full operation by 2024.

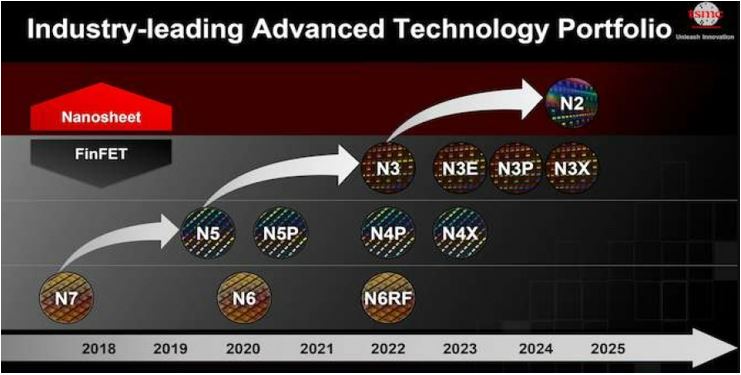
Besides expanding their production capacity, they are also investing in R&D to develop and further advance the chip technology. They have made plans to develop the process technology for 3nm and 2nm. TSMC expect to start the production of these chips by later half of 2022 and 2025 respectively.
The development process roadmap is shown in the chart below:
CHIPS ACT
The full name of CHIPS Act is known as Creating Helpful Incentives to Produce Semiconductors for America Act.

The US government has allocated USD 52.7 billion to support the semiconductor industry growth on the US soil by encouraging chip manufacturers, such as TSMC, Intel & Micron to expand their production facilities in the US.
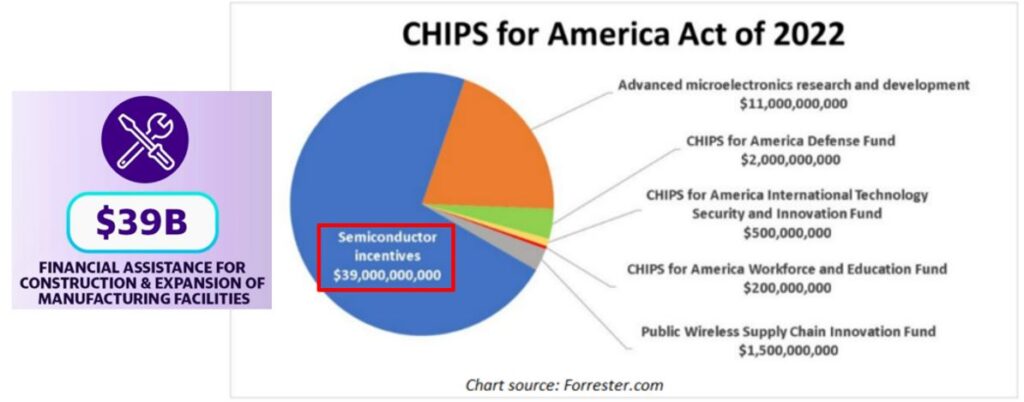
About 74% (USD 39.0 billion) of this incentive is being allocated to the construction & expansion of manufacturing facilities in the US. The remaining incentive (26%) is being allocated for R&D in advanced chip technology (7nm and below) and other areas that help to boost the chip production in the US.

However, the benefactors of this incentive are for chip manufacturers and semiconductor manufacturing suppliers because the CHIPS Act is set to revitalize the US semiconductor manufacturing industry. Chip designer companies, such as Nvidia, Qualcomm and AMD may not be eligible for this incentive as they only design the chips and are not involved in the manufacturing process of the chips.
COMPETITORS
From the semiconductor ecosystem, we learned that TSMC is categorized under the Foundry section, where this section of semiconductor companies focus on producing semiconductor chips.
When we check on the market share for semiconductor foundry companies, we found that Taiwan is currently the world’s largest chip producer (64% in 2021 & 66% in 2022F), with TSMC taking the largest chunk of the market share pie (53% in 2021 & 56% in 2022F).
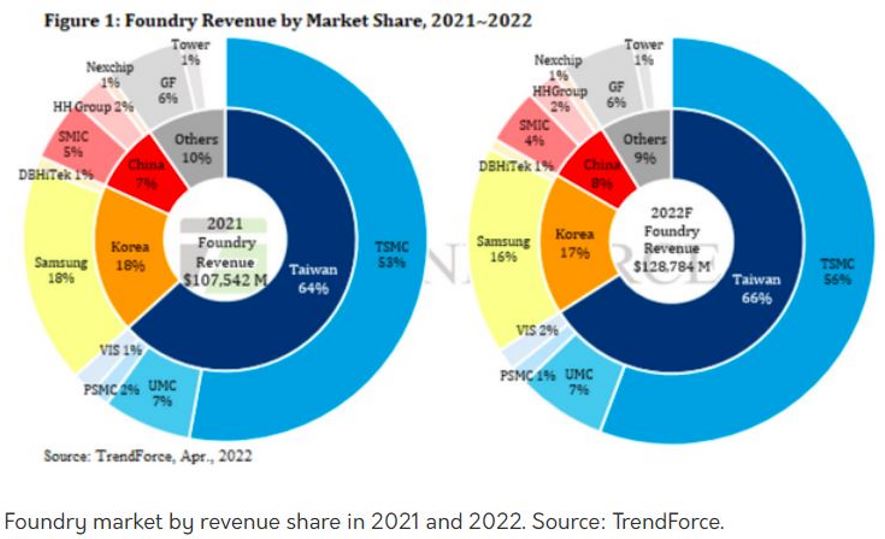
From the market share, we are also comparing the other top 4 competitors of TSMC in terms of the technology production and application markets. The top 4 competitors of TSMC are Samsung (Korea), UMC (Taiwan), SMIC (China) and Global Foundries (US).
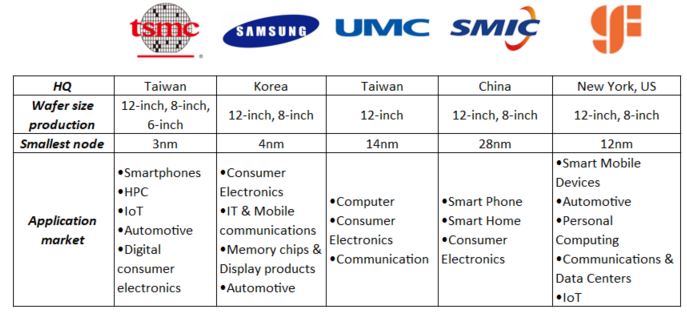
In the chart above, we observed that most of the chip makers are producing the chips from 8-inch to 12-inch wafer. However, TSMC is currently the only chip maker that is producing the smallest chip – 3nm and expected to be released to their customers in later half of 2022.
In addition to that, most of the chips manufactured are being used in consumer devices, such as smartphones and PC. For other application markets – automotive and Internet of Things (IoT), only TSMC, Global Foundries and Samsung (automotive).
ECONOMIC MOATS
Economic moat is the competitive edge that a company has against their competitors to protect their business profits and market share.
What is so special about TSMC that they are taking the largest chunk of the semiconductor foundry market share?
First, TSMC is the technology leader within the semiconductor industry as they are developing the latest and most advanced chip technology, which is 2nm.
For semiconductor chips, the lower the node figure (e.g. 2nm), the higher transistor count can be included in the chip and thus making the chip more powerful and energy efficient.
In addition to that, TSMC has files over 75,000 patent applications worldwide as of May 2022 to protect their R&D innovation & technology so that they remain the technology leader within the industry.

TSMC have a large customer base to sell their chips and the chips are being used worldwide in 5 major markets as per mentioned in the Products section. The table below illustrates the list of top 10 TSMC customers:
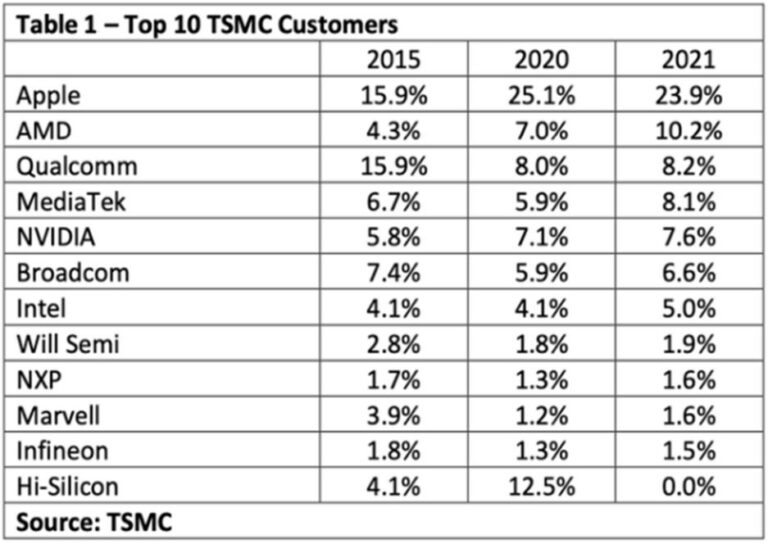
Since 2020, Apple has been TSMC’s major customer as TSMC has been supplying chips to Apple products, especially iPhone products. Other major TSMC customers are fabless companies such as AMD, Qualcomm and Nvidia where they only design the chips and outsource the chip manufacturing process to TSMC.
FINANCIALS
In this section, we will further deep dive into the numbers to find out if the company is doing well financially before we put in our money to invest.
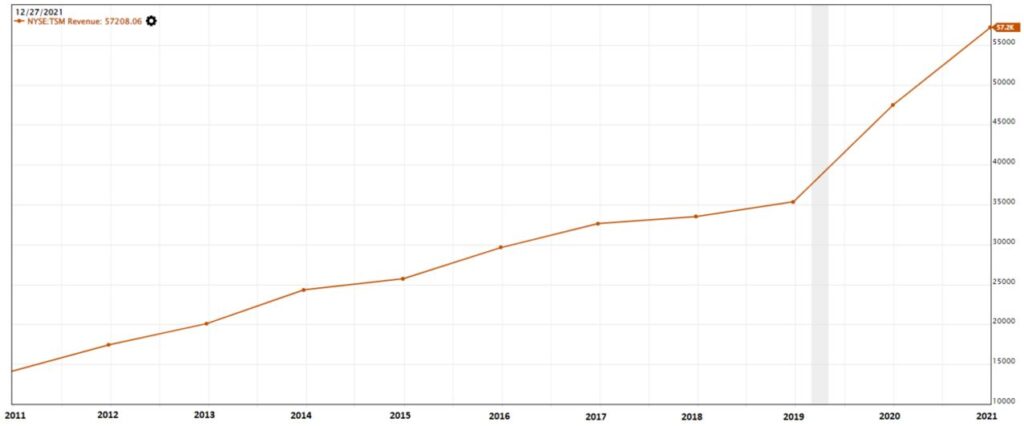
The Revenue generated for the past decade has been consistently growing in an uptrend manner. This indicates that the company sales of semiconductor chips are doing well.
Besides looking at the revenue, we also look at their Net Income to determine if the company is profitable.
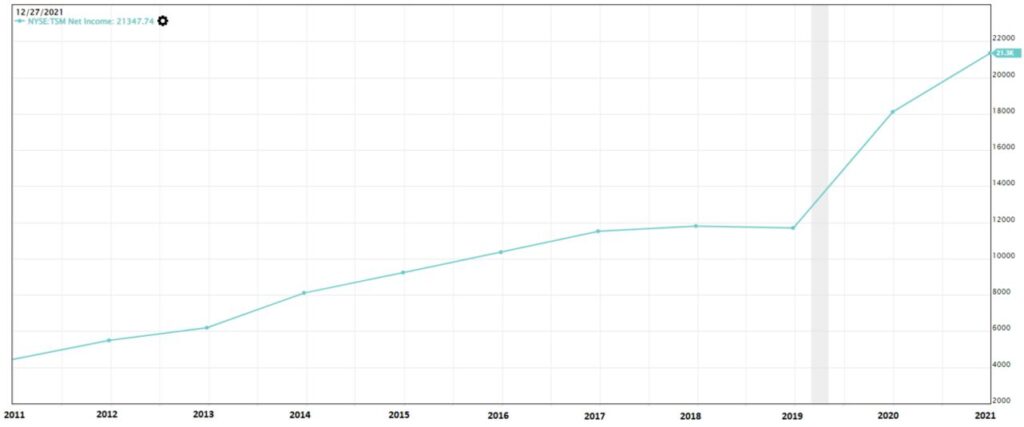
The definition of net income is how much profit or loss is the company making after deducting all the expenses to produce the chips from the revenue earned.

In the chart above, the net income trend is in an uptrend manner. However, we saw that there was a slight stagnant in profit in 2019. Further investigation in the annual report revealed that the company has increased their expenses in R&D. Nevertheless, the overall trend is positive and growing. Based on the Value Investing Criteria, this is a good sign that the company is profitable for the past decade.
Next, we will be investigating on the company’s cash flow. We will be looking at their Operating Cash Flow and Free Cash Flow.
Operating Cash Flow refers to the cash flow that was being generated from the normal business activities. When the cash flow is positive, it means that the cash is coming into the company, and if the cash flow is negative, it means that cash is flowing out from the company.
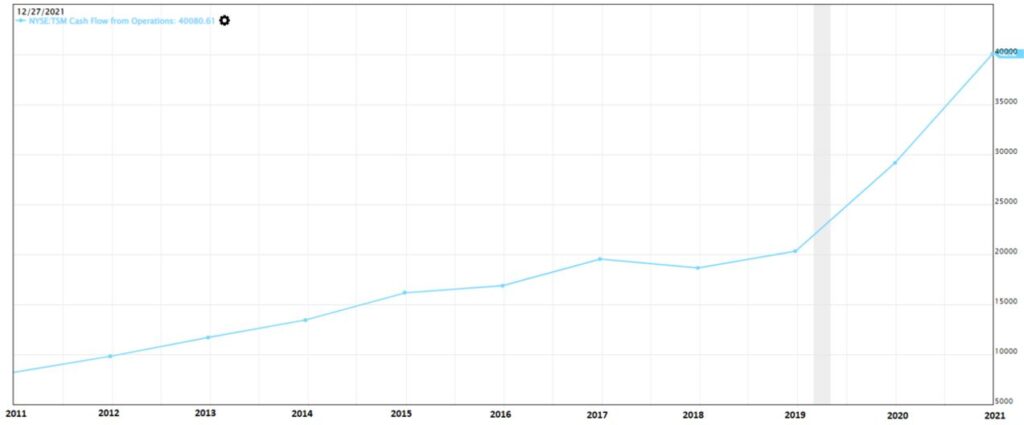
In the chart shown above, the Operating Cash Flow has been positive and in an uptrend manner. From the Value Investing methodology perspective, this is a good sign as money is coming into the company from business operations.
To further expand or maintain the production facilities, TSMC will invest money (Operating Cash Flow) on Capital Expenditure (CapEx – expenses to purchase assets that may last for more than 12 months). The money that is being left for the company to use freely is known as Free Cash Flow.
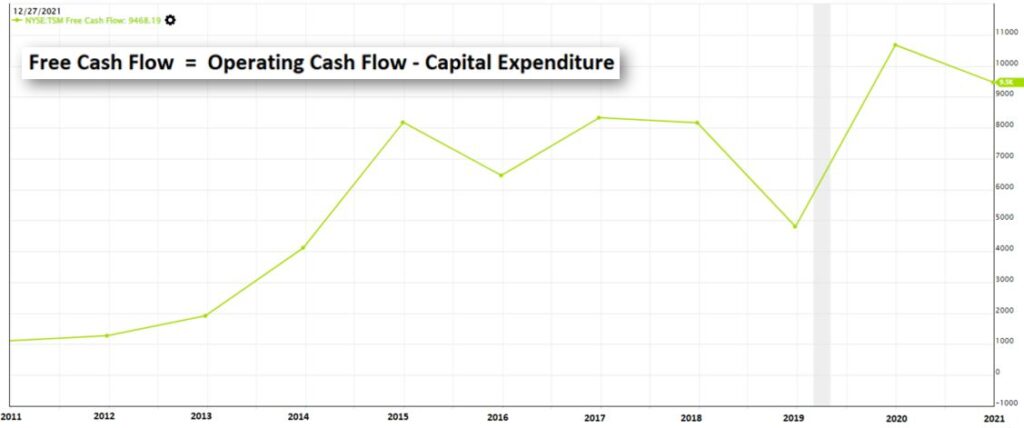
From the Free Cash Flow chart, we noticed that there was a sharp dip in 2019. In their annual report, it was reported that they have increased their CapEx in 2019 as shown in the table below.
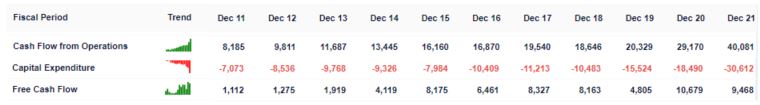
Even though the CapEx for 2020 and 2021 has increased, their Operating Cash Flow also increased. Thus, the Free Cash Flow for 2020 and 2021 also increased.
We are also curious about the debt level of the company, and we will be looking into the Debt-to-Equity ratio. The formula of debt-to-equity ratio is shown below.

Based on Value Investing Methodology, for every $100 of equity invested into the business, if the company borrow less than $50 of debt, the company is managing their debt well.
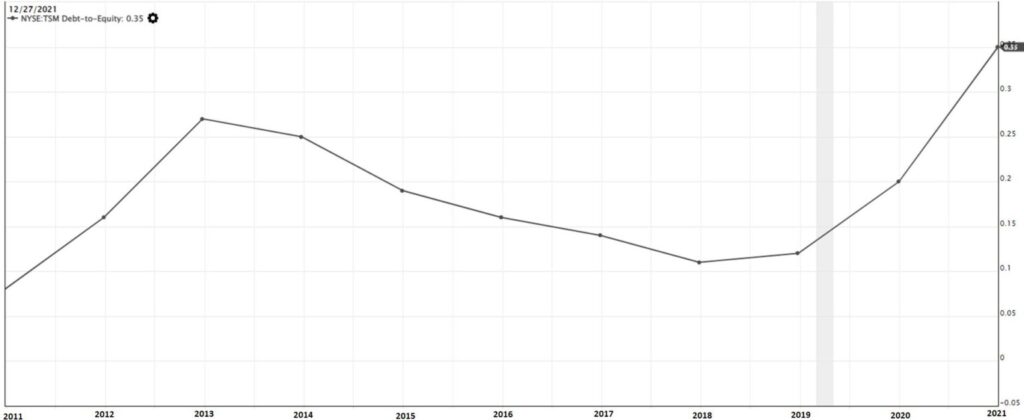
From the chart above, the debt ratio for TSMC is at 0.35 in 2021, which is below 0.5.
POTENTIAL RISKS
Even though TSMC is the world’s largest semiconductor manufacturer and leader in the advanced microchip technology, investors need to take note of the relationship between Taiwan and China as it may affect the chip production of TSMC.

Should the chips production stop due to the conflict between these two countries, it may affect the revenue generation and cash flow of the company.

Other than that, the chip sales are tightly correlated to the consumer device sales. If the consumer devices sales slowdown, the chip demand will also be affected as per reported by an article from Investor’s Business Daily.
CONCLUSION
To conclude it all, TSMC is the world’s biggest chip manufacturer with the largest customer and distribution network for their chips. With the upcoming development of 3nm and 2nm nanochip in progress, TSMC can still be seen as the technology leader within the industry.
However, as majority of chip production is in Taiwan, should there be a conflict started between Taiwan and China, it will not only severely impact TSMC business performance but also the global semiconductor chip production. When the world could not get enough of the chips, many technological devices’ production will also become paralyzed and may cause a huge damage in the economy.
For this, investors is strongly encourage to further assess the pros and cons before deciding to invest their money into TSMC. Do comment below and let us know your thoughts if now is a good time to invest in TSMC!
DISCLOSURE
The above article is for educational purposes only. Under no circumstances does any information provided in the article represent a recommendation to buy, sell or hold any stocks/asset. In no event shall ViA or any Author be liable to any viewers, guests or third party for any damages of any kind arising out of the use of any content shared here including, without limitation, use of such content outside of its intended purpose of investor education, and any investment losses, lost profits, lost opportunity, special, incidental, indirect, consequential or punitive damages resulting from such unintended use.