Since ChatGPT launched in November 2022, it has caught worldwide attention and reached 1 million users in a mere 5 days! Now crossing over 100 million users in 2 months after launch!
ChatGPT‘s surge in popularity for generating human-like responses to prompts, such as essays and code, has alarmed Google’s management and endangered their core Search Advertising revenue.
In the global race of generative artificial intelligence (AI), how will Google and Baidu compete against this latest internet sensation – ChatGPT?
In this article, we will deep dive into Google Bard & Baidu ‘Ernie Bot” to unearth the potential functions of these ChatGPT rivals!
We have also covered this topic in our YouTube Channel and also explored ChatGPT’s other potential rivals besides Google & Baidu! Click on the video to watch!
WHAT IS GENERATIVE AI?
Generative AI is a branch of Artificial Intelligence (AI) that is involved in creating new content or data from texts, music and videos or pictures. It uses various machine learning algorithms and AI techniques to create the new contents from keyword prompts, just like ChatGPT.
When people mention generative AI, language models, chatbots and conversational AI will also pop up in their mind. Although these 3 look similar at first glance, they have different functions. Let’s find out more about them!
LANGUAGE MODEL
Language Model is an AI algorithm that predicts the probability of a sequence of words in a language, which is useful in applications, such as text generation or translation. Hence, it is an AI technique that generative AI chatbots, such as ChatGPT and Google Bard installed.
As shown in the diagram below, where one keyword input into the system will trigger a myriad of responses, the AI will try to predict the next possible word based on the database that it was set up with.

Google Lamda Language Model
CHATBOTS
Before ChatGPT, the common application of generative AI can be found in Chatbots. Chatbots are rule-based conversational AI where they can answer queries and reply back from a predetermined script and database.
These chatbots are very useful in the customer service field where they can handle a few questions simultaneously over chats and provide the answers immediately to customers, such as stock availability in a retail store or solutions for the problem that the customer is having.
This can cut down the waiting time for customers who are seeking help and also minimize the number of manpower in the customer service organization of a company!
However, as these chatbots can only answer from predetermined script, if we were to ask anything outside of their scope of understanding, they won’t be able to help us with our questions and keep on repeating the same reply. This has created frustration among the customers and may trigger the emotion of throwing the keyboard across the room.
To overcome the inflexible and robotic response from chatbots, engineers further enhanced the language model techniques and developed an improved version of conversational AI.
CONVERSATIONAL AI
Conversational AI is an upgraded version of chatbots where they can understand, deduce the meaning and intent in a dialogue and respond to human language.
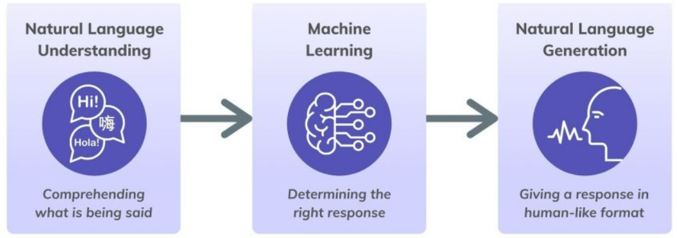
With the upgraded functions, these conversational AIs are capable of handling more complex tasks, such as providing appropriate feedback to their human counterpart instead of predetermined script. An example of conversational AI is J.A.R.V.I.S in the Iron Man movies where it not only handles Tony Stark’s schedule but also manages his garage of numerous Iron Man armours.
HOW WILL GENERATIVE AI REVOLUTIONIZE THE WAY WE WORK?
With the advancement of generative AI in recent years, it has been touted to have massive potential to increase work efficiency, productivity and innovation in various fields.
Here are some of the tasks & applications that will benefit from the revolution of generative AI:
- Generate creative ideas and explore new possibilities for content creation.
- Enhance customer experience for online shopping by providing personalized recommendations.
- Improve customer support with faster response time and provide accurate information.
- Automate repetitive tasks such as data entry and label imaging for stock inventory.
- Improve decision making by generating predictive simulation models, such as pricing models or marketing strategies
POTENTIAL RISKS OF GENERATIVE AI
The rise of generative AI has brought both the pros to mankind’s workforce by increasing work productivity, and also the cons of the potential to significantly impact the job market.
In this article by Business Insider, it has listed out 10 roles that may be replaced by AI.

As generative AI becomes more sophisticated and may replace certain jobs, it may also have the potential to spread misinformation or fake news that might trigger significant social and political consequences. This phenomenon is known as machine hallucinations.

Machine hallucinations is the ability of machines to generate images or text contents that are not real but appear highly realistic or plausible. While generative AI can produce realistic simulations and synthetic data, it also raises ethical and security concerns, such as the potential for deception and accepting misinformation as factual.
As generative AI becomes more widespread, it’s crucial to weigh the risks and benefits and establish safeguards against potential misuse.
With the popularity of ChatGPT rising and the potential to threaten their #1 position in search advertisement for the past decade, Google has announced that they will release their own version of AI-powered chatbot, known as Google Bard to rival against ChatGPT.
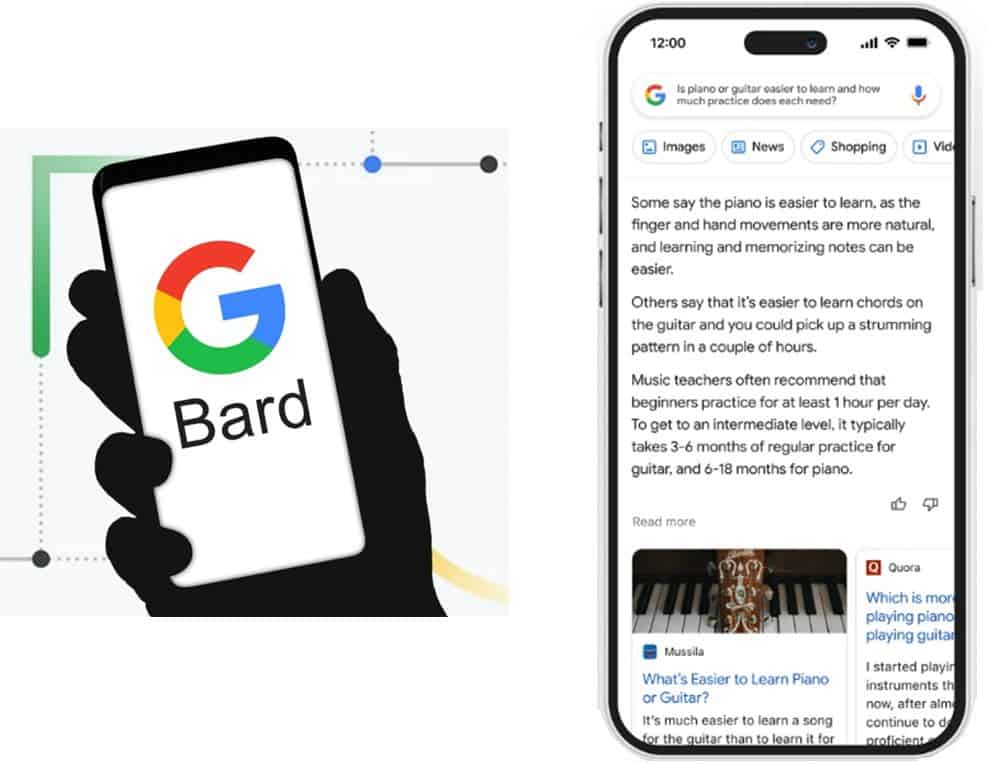
GOOGLE BARD
Google Bard is built on Google’s existing large language model – Lamda where it can find information and answer in human-like responses.
When comparing against ChatGPT, one of the potential advantages that Google Bard has over ChatGPT is the latest information that they can generate.
Google Bard has access to its existing massive database and is capable of gathering information from the most recent and up-to-date materials. Whereas ChatGPT knowledge cutoff date is September 2021, any information after 2021 was not able to be provided.
In addition, it is also being programmed to compile the complex information into easy-to-digest formats for easier reading and understanding.
GOOGLE AI PROJECTS
Google, being one of the leading companies in developing AI technologies is also involved in various AI projects besides language model Lamda.
These AI projects are categorized under their Other Bets segment where it is mainly focused on investing in companies that are further developing the AI technologies.
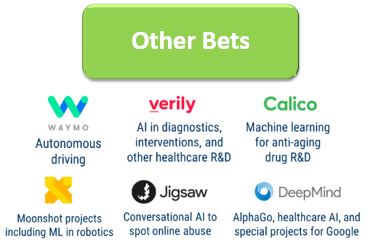
As of Mar 2023, Google is currently involved in 24 AI projects, with 7 projects that are intertwined in creating Google Bard.
Google’s current on-going 24 AI projects
BAIDU
Baidu, China’s largest internet search engine and leading AI company, has also announced the launch of ChatGPT-style ‘Ernie Bot’ where they expect to release to the public after completing internal testing in March.

Ernie Bot is rumored to utilize conversational language modeling technology where it can:
- Display exceptional understanding of what was being said
- Integrate extensive knowledge with massive data
- Formulate reasonable and coherent texts from the knowledge database
This sounds similar to ChatGPT functions!
Currently, Ernie Bot is getting more attraction in China as ChatGPT is not allowed for registration for Chinese users. More companies, including Chinese media outlets are approaching Baidu to set up their own intelligent chatbots with Ernie bot technology.
BAIDU AI PROJECTS
As the leading AI company in China, Baidu is heavily involved in various AI projects as they use AI to provide large information and knowledge-centric contents to the Chinese public.
Baidu Brain is an advanced intelligent AI platform designed to process all forms of content via AI technology. It provides a comprehensive AI infrastructure for building and deploying advanced technologies, such as machine learning algorithms and deep learning.

With Baidu Brain, the major AI initiatives that Baidu take on includes:
- Apollo – Autonomous driving platform to develop self driving cars in urban environments.
- Baidu Wangpan (previously known as Baidu Cloud) – Cloud computing platform to run various AI-powered applications, such as chatbot development tools.
- DuerOS – Voice-activated digital assistant, which is similar to Apple’s Siri and Amazon Alexa.
- Baidu Health – Baidu’s healthcare division where it uses AI to develop new diagnostic tools, predict disease outbreaks and improve patient care.
As investors, we love to seek out new opportunities to invest in good companies. Is Google and Baidu a good company to invest in now with the launch of their own version of ChatGPT-like chatbots?
We have done a quick screening analysis about the company background and financial numbers in our YouTube Channel. Click on our video to find out!
CONCLUSION
All in all, we can see the massive potential of generative AI in improving work productivity.
Nevertheless, one should always take note of how the technology is being used in their daily lives as generative AI is just a powerful tool that can either help us to work more efficiently or become a lethal destructive weapon if it is used in the wrong hands.
If you have always wanted to determine good investing opportunities based on your own analysis, click on the banner below “Masterclass Registration” to join our upcoming masterclass to learn more about our simple and yet systematic way to analyze companies based on Value Investing Methodology!
DISCLOSURE
The above article is for educational purposes only. Under no circumstances does any information provided in the article represent a recommendation to buy, sell or hold any stocks/asset. In no event shall ViA or any Author be liable to any viewers, guests or third party for any damages of any kind arising out of the use of any content shared here including, without limitation, use of such content outside of its intended purpose of investor education, and any investment losses, lost profits, lost opportunity, special, incidental, indirect, consequential or punitive damages resulting from such unintended use.