When interest rates were hiked up by the FED in 2022 to combat inflation, it put tremendous pressure onto the banks. This might have caused the liquidity crisis of Silicon Valley Bank (SVB) and instigated a bank run which led to its downfall.

Other than SVB, other US regional banks also fall victim due to the high interest rates environment. The domino effect of lost confidence in the banks have led to one bank failure to another, from US’s Signature Bank to the latest casualty of the scandal-ridden Swiss bank – Credit Suisse.
With several banks’ downfall and confidence in the banking system at an all-time low, will it lead to another banking crisis?
In this blog article, we will explore the recent bank collapses and compare them against the ’08 – ’09 Global Financial Crisis to determine if a repeat of the banking crisis is around the corner.
We have also covered this topic and compared both financial crisis in our YouTube Channel. Click on to watch!
If you are interested in bank stocks, we have covered the following banks below! Click on the link to find out more!
'08-'09 GLOBAL FINANCIAL CRISIS (GFC)
The ’08 – ’09 Global Financial Crisis (GFC) was a severe worldwide economic downturn that started in 2008 and lasted until 2009. The crisis was triggered by the collapse of the US housing market, which further led to the failure of several major financial institutions, such as Lehman Brothers and Bear Stearns.
What had caused this appalling financial crisis to happen?
In the years leading up to the crisis, there was a rapid increase in the number of subprime mortgages, which were loans given to borrowers with low credit scores. These mortgages were then bundled together and sold as high yield mortgage-backed securities (MBS) to investors. High demand for these MBS also led to the inflation of the housing bubble in the US as more borrowers with poor credit histories can buy their dream home.
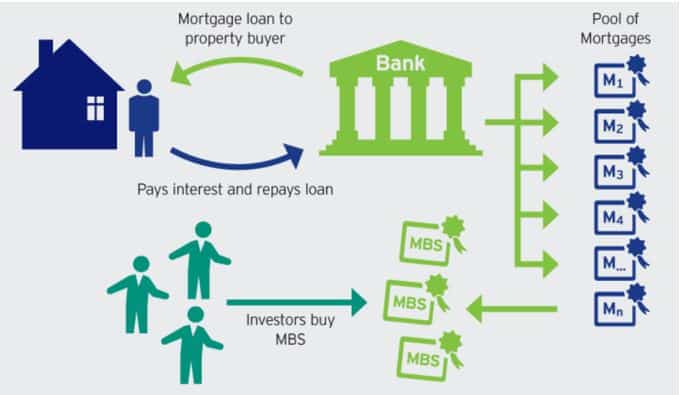
Creation of mortgage-backed securities (MBS)
However, as more and more homeowners defaulted on their mortgages due to increasing mortgage rates, the value of these securities plummeted and the housing bubble burst. This caused huge losses for banks and investors who held onto MBS.
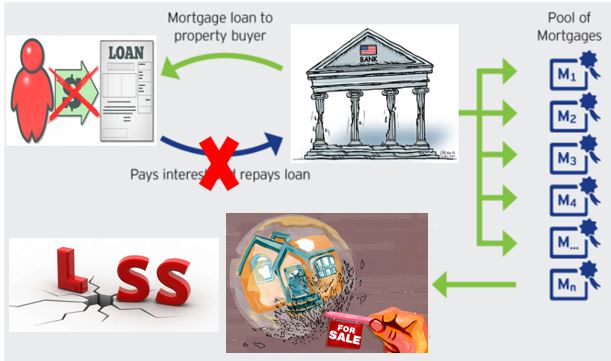
Homeowners default their mortgages and led to loss value of MBS
The crisis quickly spread beyond the housing market, as major financial institutions that held large amounts of these securities began to fail.
The ripple effect spread across the globe, causing a credit crunch and freezing up the flow of credit in the banking system. Due to the severe economic consequences, governments around the world intervened by providing financial support to certain failing banks to stimulate economic growth. This is known as government bailouts.
COLLAPSE OF LEHMAN BROTHERS
During the credit crunch, some of the banks were able to receive bailouts, such as Citibank but others were left bankrupt, which was the infamous Lehman Brothers.

Collapse of Lehman Brothers
Now the question arises:
“Why was there a discrepancy between financial institutions where one was to be “saved” and not the other?”
This is because Lehman Brothers is an investment bank where they mainly help their clients to reinvest their deposits.
To generate higher returns for their clients, they had taken on high debt to finance their operations and investments. Thus, they had a concentrated portfolio of high-risk assets where one of the portfolios was invested heavily into MBS.
When the housing bubble burst, the bank encountered a liquidity crisis. This had triggered concern among investors about the bank’s exposure to subprime mortgages.
Fear of their capital loss, many investors withdrew their funds to protect their capital and the incident escalated to bank run. The bank did not receive a bailout from the government and was allowed to go bankrupt.
BAILOUT OF CITIBANK
Citibank has many diversified business operations where its banking operation involves retail banking, commercial banking, and investment banking.
Hence, Citibank has a larger portfolio of assets which also indirectly helped them to cushion against the impact of the financial crisis.
Like Lehman Brothers, Citibank was also exposed to MBS where they borrowed heavily to finance the investments in the subprime mortgage market.
When the borrowers defaulted on their mortgage loans, the bank was caught in the catastrophe. They too suffered significant losses when the MBS value plummeted. The bank struggled to meet debt obligations and had to face margin calls.
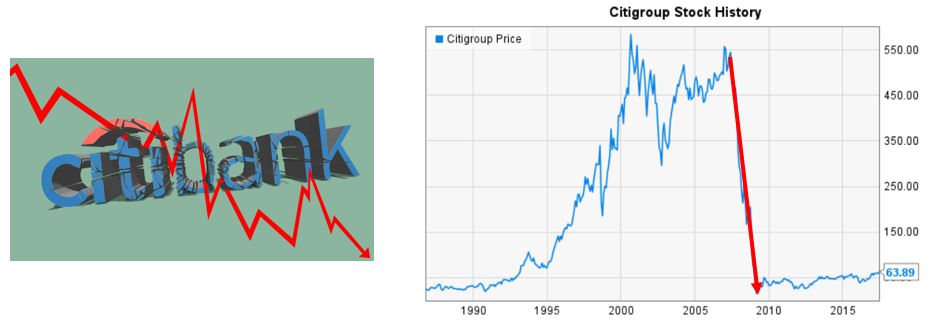
Citigroup stock plunged during GFC
Fortunately for Citibank, they were able to receive a bailout from the government from this financial fiasco. This is because the bank was seen as “too big to fail”. Should Citibank collapse, it will have more severe economic damage consequences on the financial system.
2023 BANKING CRISIS
Now let’s turn our attention to the latest banking crisis that has unsettled the financial world and set off a tsunami of fear among the public, with the near collapse of the financial institutions during the GFC still fresh in mind.
The latest banking crisis started when several regional US banks were reported to collapse after a bank run had happened. People were scrambling to withdraw their money from the bank, concerned that they may lose their life savings or company’s working capital.
One of the banks was Silicon Valley Bank (SVB).
COLLAPSE OF SVB
Silicon Valley Bank was a leading commercial bank for startup companies in the tech industry and healthcare firms.
During the tech industry booming in 2021, the bank received large amounts of deposits from their clients and reinvested those monies into long-term Treasury bonds.
However, when the FED increased the interest rates to combat the high inflation in 2022, the bonds declined in value. Thus, SVB had a significant number of unrealized losses.
When the news broke out, investors and depositors lost faith in the bank and immediately withdrew their deposits. To fulfill the request of sudden mass withdrawals, SVB had to sell the bonds at a loss of $1.8 billion which further ruffled the public’s concern about the banks’ financial health.
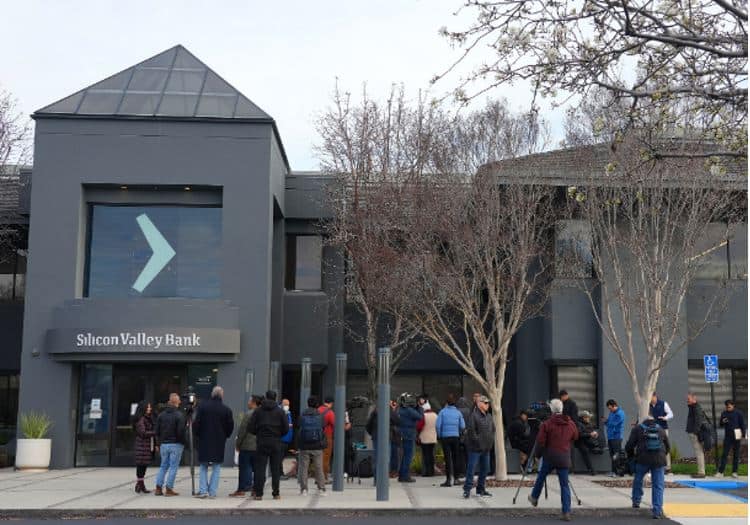

Bank run at SVB
This led to a massive bank run and the bank encountered a liquidity crisis where the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC) had to step in to stop the panic.
Other than SVB, other banks such as Signature Bank and Silvergate Bank also collapsed like a domino effect in this latest banking crisis.
The contagion of bank collapses in the US has spread to Europe, which brought down Credit Suisse.
COLLAPSE OF CREDIT SUISSE
Credit Suisse was one of the world’s leading financial institutions, headquartered in Zurich, Switzerland. It offers a range of financial services, mainly in investment banking, private banking, asset and wealth management to individuals, corporations, and institutions around the world.
With a history dating back to 1856, Credit Suisse has established itself as a leading player in the global financial industry, serving clients in over 50 countries. The bank has a strong reputation for its expertise in investment banking and often ranked among the top banks in this field.
Despite its global presence, Credit Suisse has faced several challenges in recent years. Its reputation was further tarnished by self-inflicted scandals and mismanagement as shown in the diagram below.
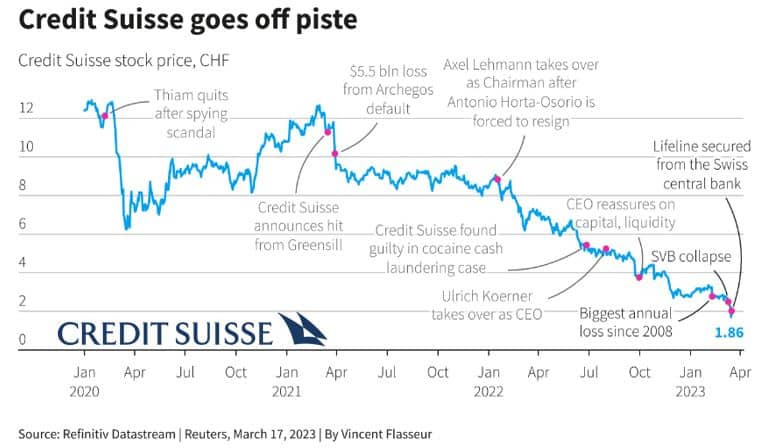
Debilitating events that led to downfall of Credit Suisse
When SVB collapsed, the bank was still struggling to stand back on its feet from the devastating news that the bank had suffered the biggest annual loss since 2008.
Various news channels had turned their limelight on Credit Suisse, broadcasting the worsened financial health of the bank and predicting its demise.
The final nail to the coffin was when the bank’s largest investor, Saudi National Bank refused to inject more money into the bank. Investors got cold feet and began pulling out their money from the bank.
Credit Suisse had to turn to the Swiss Government for assistance to boost their liquidity and to reassure the nervous public that the bank’s financial was still good.
Nevertheless, the Swiss Central Bank had arranged a takeover by the bank’s rival, UBS. This had led to the downfall of the iconic Swiss Bank which had existed for 167 years.
COMPARISON BETWEEN GFC & BANKING CRISIS 2023
DIFFERENCES
From the sequence of events of the bank failures, we learned that the trigger points for the ‘08-’09 GFC and the 2023 banking crisis are quite different.
The GFC was primarily caused by the high number of borrowers who defaulted on their mortgage payments. This led to a significant decline in the value of mortgage-backed securities and other financial instruments. The ripple effect was escalated throughout the financial industry, leading to a widespread liquidity crisis and the collapse of several large financial institutions.
On the other hand, the 2023 banking crisis was triggered by the high interest rates that put pressure on banks, especially for banks that had their deposits locked in long-term bonds. As the investors grew worried about the banks’ financial health, they demanded withdrawal of their money.
The massive withdrawal within a short period of time eventually led to a bank run and the banks suffered from liquidity crisis. Liquidity crisis happened when the banks did not have sufficient cash for money withdrawals and caused the banks to collapse.
SIMILARITIES
On the other hand, although these two financial crises occurred in different contexts and for different reasons, they do share some important similarities.
One similarity is the issue of concentrated risk. Lehman Brothers had a highly concentrated portfolio of high-risk assets, while SVB had a concentrated customer base in the tech and healthcare startup industries. In both cases, this concentration made the banks vulnerable to external factors, such as changes in the market condition or the economy.
As such, both banks experienced a loss of confidence from their customers and investors during the downturn of events, which led to a bank run. This loss of confidence can be a significant challenge for any bank or financial institution, as it can lead to a self-fulfilling cycle of withdrawals and declining liquidity.
Overall, these crises highlight the importance of diversification and risk management in the banking industry. In addition, it is also important to maintain customer and investor confidence in the financial system when facing external challenges, such as a high interest rate environment to prevent widespread economic damage.
HOW SHOULD YOU PROTECT YOUR MONEY?
Some of us might be concerned that “How can we better protect our money?” when the financial systems are under high uncertainty during these trying times.
To protect your money from a banking crisis, it’s important to understand the Deposit Insurance Scheme (DIS) in Singapore. The DIS is a government-backed program that provides insurance coverage for deposits held in eligible financial institutions in Singapore, including banks, finance companies, and insurance companies.
SDIC Website
Under the scheme, each depositor is insured up to S$75,000 per financial institution. This means that if a bank were to fail, depositors would be able to recover their deposits up to the insured amount.
If you have multiple accounts with the same bank, your total insured amount would be capped at S$75,000, regardless of how many accounts you have. For example, if you have three accounts with the same bank, each with S$30,000, only S$75,000 of your total deposits would be insured.
If you have accounts with multiple banks, each bank would be insured separately up to S$75,000 per depositor. This means that if you have deposits in two banks, each with S$50,000 for example, both deposits would be fully insured under the DIS.
It’s important to note that the DIS only applies to deposits held in eligible financial institutions and does not cover other types of financial products, such as investments or insurance policies. Thus, one should check on the DIS website’s list of DI Scheme Members to find out if their money stored in the financial institutions is covered under this scheme.
By understanding the DIS and taking steps to protect your finances, you can take one step further to safeguard your money against potential banking crises and other financial risks.
CONCLUSION
Even though it is every depositor’s nightmare to lose their life savings when a bank collapses due to bank run, one should always save their money in a reputable financial institution that is protected under government-backed schemes, such as the DIS.
Moreover, it’s essential to diversify one’s investments and consider other forms of financial protection, such as insurance policies or investment portfolios, other than saving a part of your money in the bank.
If you have always wanted to learn how to invest but not sure how to get started in Singapore, fret not!
Join us in our Masterclass where we will teach you how to kick start your investing journey in a systematic and safe manner with Value Investing Philosophy.
Click on the banner below to kickstart your investing journey!
DISCLOSURE
The above article is for educational purposes only. Under no circumstances does any information provided in the article represent a recommendation to buy, sell or hold any stocks/asset. In no event shall ViA or any Author be liable to any viewers, guests or third party for any damages of any kind arising out of the use of any content shared here including, without limitation, use of such content outside of its intended purpose of investor education, and any investment losses, lost profits, lost opportunity, special, incidental, indirect, consequential or punitive damages resulting from such unintended use.